Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
PM’s address highlights:
‘Save Soil Movement’ is a global movement to increase awareness about deteriorating soil health and bring about a conscious response to improve it.
Soils in India:
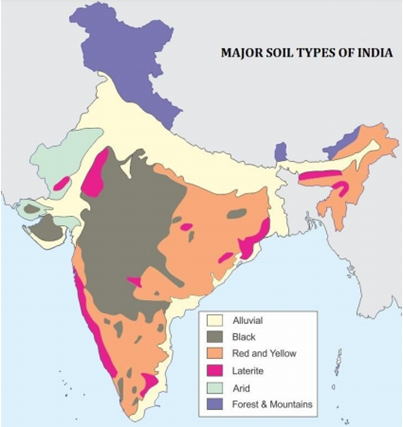
India has varied relief features, landforms, climatic realms and vegetation types. These have contributed in the development of various types of soils. Indian soils are largely deficient in nitrogen, mineral salts, humus and other organic materials. On the basis of genesis, colour, composition and location, the soils of India have been classified into:
Copyright infringement not intended.
Alluvial Soil
Coverage: 15 lakh sq km (46 per cent of the total area).
Parent Material: Himalayan Rocks (Hence, Transported Soil- Brought by rivers)
Type: Immature and azonal Soil (Since, of Recent Origin)
Nature:
Chemical Composition:
Distribution: Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal
Crops: Rice, Wheat, Sugarcane, Cotton, Oilseeds and Jute
Black Soil (Regur)
Coverage: 5.46 lakh sq km (16.6 % of total geographical area)
Origin: Weathering of volcanic rocks
Parent Material: Gneisses and schists; weathering of Basaltic rock formed due to solidification of lava.
Type: Mature and zonal Soil
Nature:
Composition
Distribution: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu
Crops: Cotton, Sugarcane, oilseeds and Tobacco, jowar, linseed, virginia tobacco, castor, sunflower and millets. Rice and sugarcane are equally important.
Red Soil
Coverage: 3.5 lakhs sq km (10.6% of the total geographical area of India).
Parent Rock: Decomposition of granite, gneiss and metamorphic rocks. Formed in Low rainfall areas.
Nature:
Composition:
Distribution: Whole of Tamil Nadu, parts of Kerala, and Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Chota Nagpur plateau; parts of south Bihar, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh; Aravalis and the eastern half of Rajasthan (Mewar or Marwar Plateau), parts of North-Eastern states.
Crops: Bajra, maize, pulses, potatoes, fruits, cotton, wheat, rice, millets, tobacco, oil seeds.
Laterite Soil
Coverage: 2.48 lakh sq km
Parent Rock: Leaching of laterite rocks. Conditions - High temperature and heavy rainfall with alternate wet and dry periods.
Nature:
Composition
Distribution: Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Odisha, summits of Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, the Rajmahal Hills, Vindhyan, Satpuras and Malwa Plateau.
Crops: Plantation Crops - Cashew, Tapioca, Coffee and Rubber, cinchona, coconut, arecanut, etc.
Forest – Mountain Soils
Coverage: 2.85 lakh sq km or 8.67% of the total land area of India.
Genesis: Deposition of organic matter derived from forests
Nature:
Acidic
Composition
Distribution: Himalayan region. Western and Eastern Ghats
Crops: Wheat, maize, barley, Temperate fruits, spices, tea, coffee
Arid and Desert Soil
Coverage: 1.42 lakh sq km (4.32%).
Nature:
Composition:
Distribution: Rajasthan, Punjab and Haryana
Crops: Drought resistant barley, cotton, millets, maize and pulses are grown.
Saline Soil (Usara Soil)
Formation: Accumulation of soluble salt
Nature:
Composition:
Distribution: Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan and Maharashtra
Crops: Barseem, Dhaincha and leguminous crops
Peaty and Marshy Soil
Nature:
Composition:
Distribution: Kottayam and Alappuzha districts of Kerala(Kari soil); Odisha and Tamil Nadu, Sunderbans of West Bengal, in Bihar and Almora district of Uttarakhand.
Crops: Paddy cultivation
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved