Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: No copyright infringement intended.
Context
About
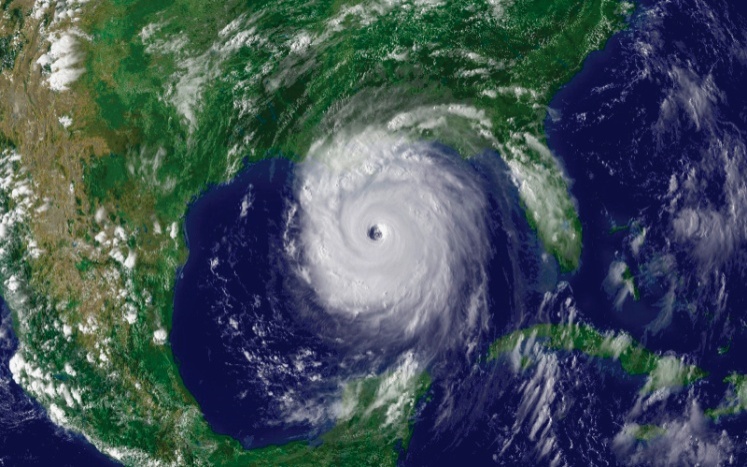
Tropical Storms
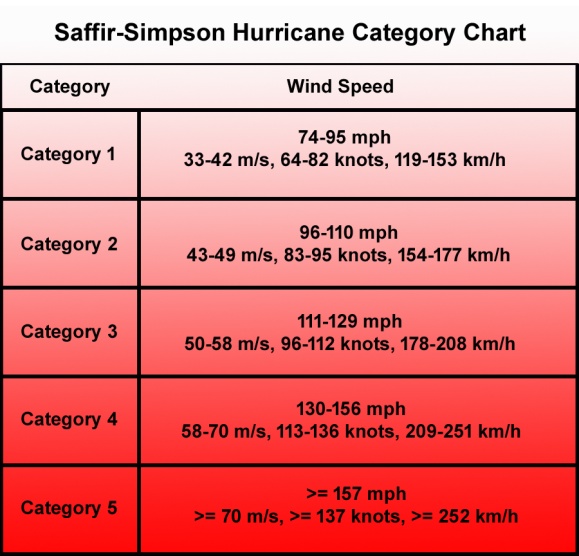
A storm must attain a sustained wind-speed of at least 240 kmph in order to be classified as a super typhoon.
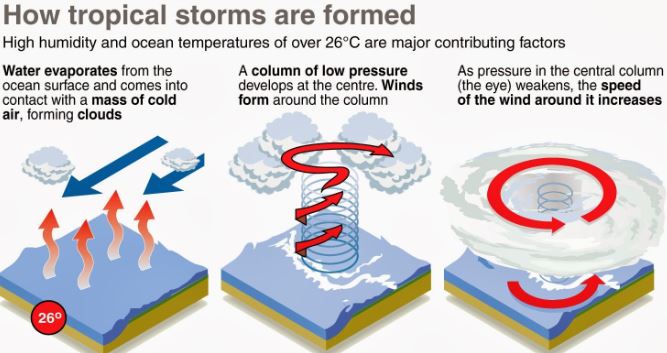
Favorable Conditions required
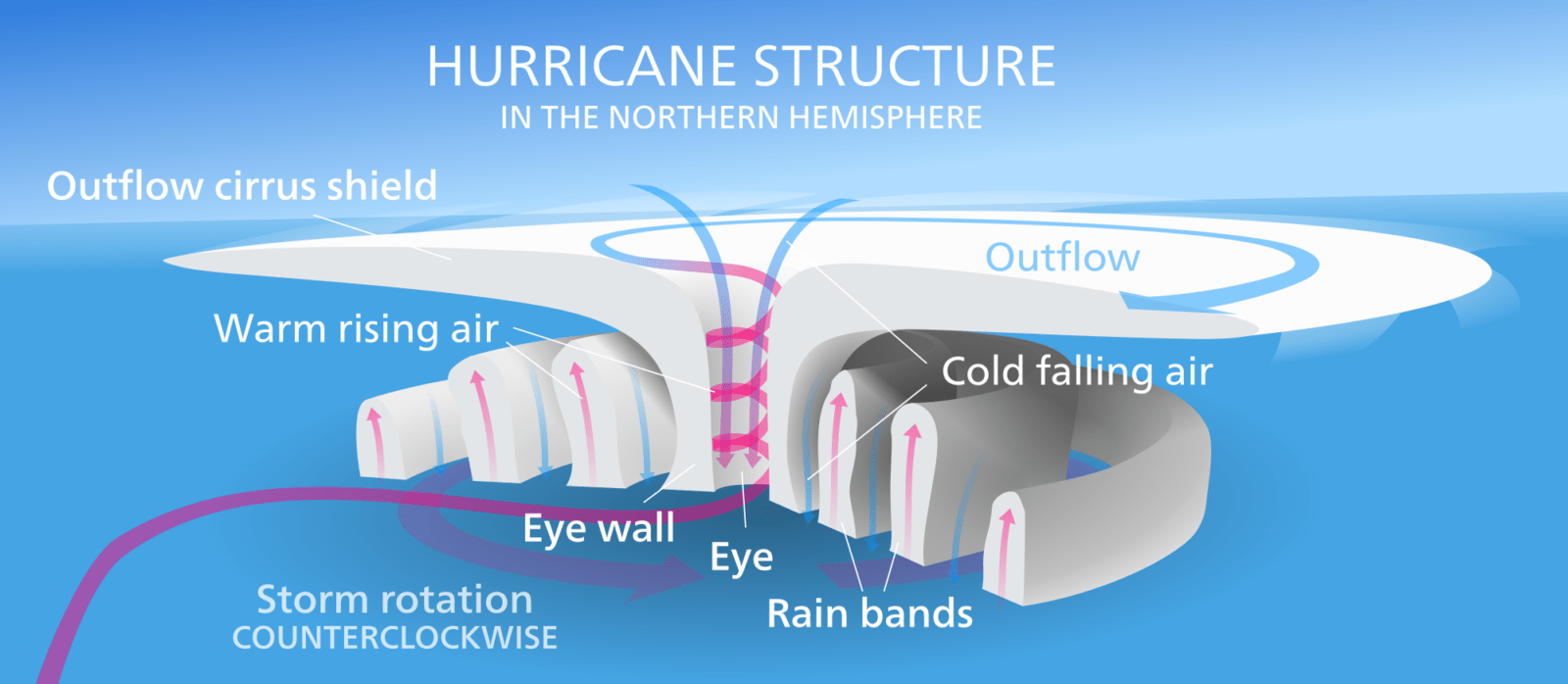
|
KEY CONCEPTS Coriolis Effect The Coriolis effect is the apparent acceleration of a moving body as a result of the Earth's rotation. It makes things (like planes or currents of air) traveling long distances around the Earth appear to move at a curve as opposed to a straight line. The Coriolis effect is an important determinant of wind direction on a global scale.
Wind shear Wind shear sometimes referred to as wind gradient, occurs when there is a change in the direction or speed of wind usually at short distances. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction of winds at increasing heights in the atmosphere. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with change in lateral position for a given altitude. For cyclones to develop, low vertical wind shear is a must.
Atmospheric Instability Atmospheric stability determines whether or not air will rise and cause storms; sink and cause clear skies; or essentially do nothing.
Atmospheric instability If an air parcel is warmer than its surrounding environment, then it will be less dense than its surroundings and will rise like a hot air balloon. This is Unstable Air and has the potential for creating thunder storms if it contains enough water vapor.
If an air parcel is cooler than its surrounding environment, then it will be denser than its environment and will sink. Think of this situation as a pebble sinking in water. This is Stable Air which generally leads to clear skies.
If an air parcel is the same temperature as its surrounding environment, then the parcel will not move of its own accord. This is Neutral Air. |
Key Components
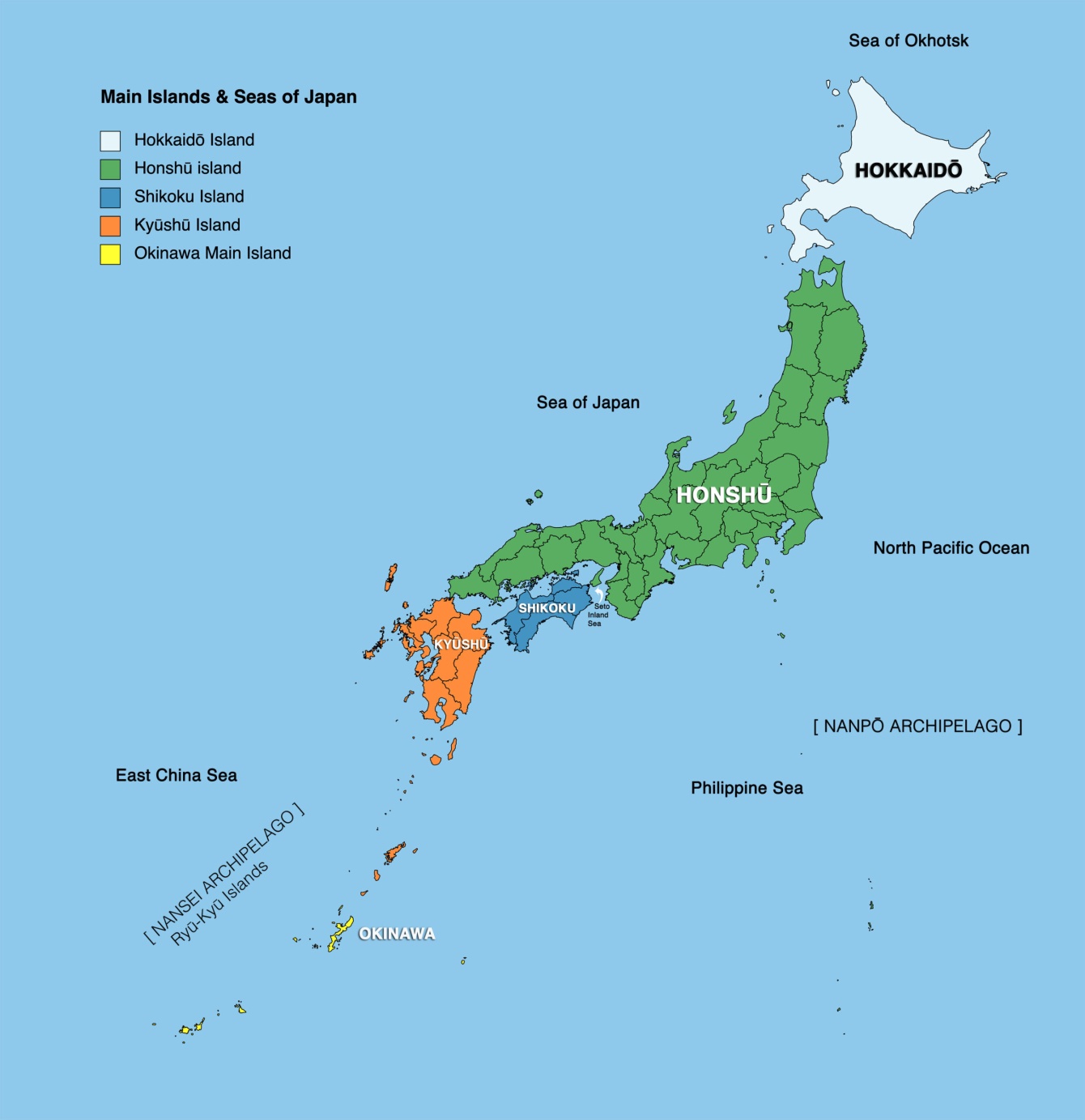
Main Islands of Japan
Okinawa is located between the East China Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, it is the largest and most populated on the 72 islands in the chain that make up the Ryukyu Archipelago.
Shikoku has high mountains and steep slopes, which limit habitability. Shikoku is the smallest of the main islands in the Japanese Archipelago.
Kyushu is a mountainous island, with many signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas with hot springs and volcanoes. The island houses Japan's most active volcano, Mt. Aso.
Hokkaido is the northernmost and largest prefecture in Japan. Hokkaido has a major role in agriculture, ranking first in Japan in production on a number of products like corn, beef, and wheat.
Honshu is the largest and most populous island in the Japanese archipelago and the seventh-largest island in the world. Honshu features many rivers, including the longest one in Japan the Shinano River.
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved