Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Trend of Swing Trading:
Understanding Swing Trading:
What is Swing Trading?
In its simplest form, traders hold on to securities for an extended period of time to earn a profit. This can range from overnight to several weeks. The objective of swing trading is to identify a trend and find swings within that trend to make a profit. Technical analysis can be used to identify these swings and act on them. Both day trading and swing trading have higher risks and costs than typical investments.
How Does it Work?
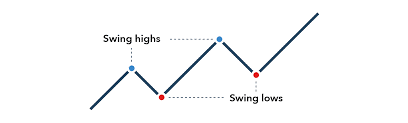
Objective of Swing Trading:
Swing trading is often undertaken by individuals and not large institutions as large institutions trade in large volumes, making it harder to enter and exit the market as required. It is a great option for beginner traders as it allows them to gain experience in trading. Losses can be kept minimal with stop-loss techniques and it provides perspective on both short and long-term trading.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Versatility:
Opportunity Identification:
Lower Losses:
Enhanced Trade Understanding:
Disadvantages:
Unpredictable Changes:
Expert Knowledge Requirement:
Psychological Challenges:
Bullish and Bearish Swing Tactics
Bullish Traders:
Bearish Traders:
Closing Thoughts
|
Relative Strength Index (RSI) The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a widely used momentum oscillator in technical analysis that measures the speed and change of price movements of a security. Developed by J. Welles Wilder, RSI helps traders assess whether a stock is overbought or oversold, thus indicating potential reversal points in price trends. The calculation of RSI involves comparing the magnitude of recent gains and losses over a specified time period, typically 14 days. This comparison is used to generate a value that ranges between 0 and 100. A reading above 70 is typically considered overbought, suggesting that the security may be due for a price correction to the downside. Conversely, a reading below 30 is often interpreted as oversold, indicating a potential rebound in price. Traders often utilize RSI to identify buy or sell signals, divergence between RSI and price movements, and the strength of a trend. By incorporating RSI into their analysis, traders can make informed decisions about entry and exit points, as well as gauge the potential direction and magnitude of price movements. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a popular trend-following momentum indicator used in technical analysis to identify potential buy or sell signals. Developed by Gerald Appel, MACD consists of two main components: the MACD line and the signal line, along with a histogram that represents the difference between the two lines. The MACD line is calculated by subtracting the 26-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA. The signal line, often a 9-period EMA of the MACD line, helps traders confirm potential buy or sell signals generated by the MACD line. Positive MACD values indicate bullish momentum, while negative values suggest bearish momentum. Traders use MACD to identify trend direction, potential trend reversals, and to confirm buy or sell signals generated by other indicators, making it a valuable tool in analyzing market trends and making informed trading decisions. |
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Explain the concept of swing trading in the context of financial markets. Discuss the benefits and challenges associated with swing trading compared to other trading strategies. Evaluate its role in facilitating short- to medium-term gains for investors and its impact on market dynamics. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved