Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


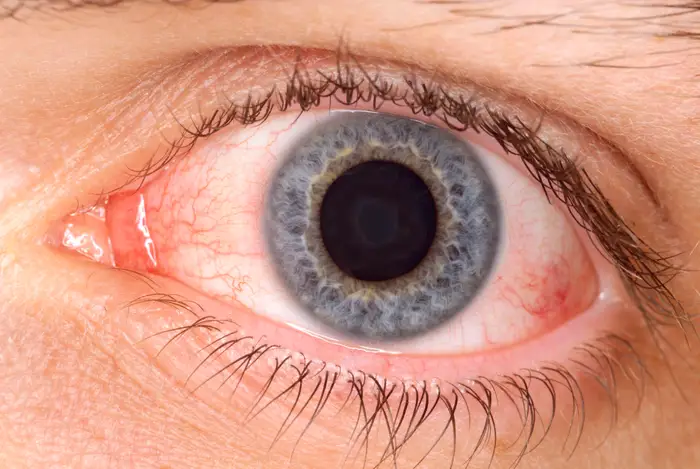
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.insider.com
Context: Ocular syphilis, if untreated, can lead to severe damage in diverse eye structures, such as the cornea, iris, retina, and optic nerve, posing risks to multiple organ systems over time.
About Syphilis
Origin of Syphilis of the eye
Transmission of Syphilis of the eye
Symptoms of Syphilis of the eye
Cure for Syphilis of the eye
Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What is the primary cause of ocular syphilis? A) Bacterial infection B) Viral infection C) Fungal infection D) Parasitic infection Answer: A Explanation: Ocular syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which is responsible for syphilis. |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved