Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


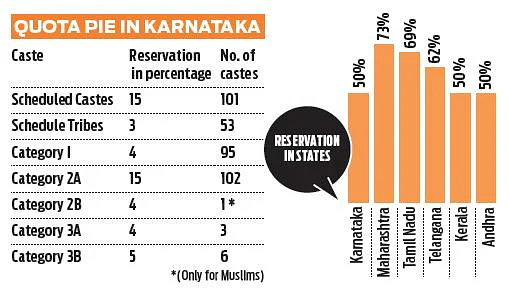
Copyright infringement not intended
In News
Why State asked the Union to include the bill in the 9th Schedule?
What is the Ninth Schedule?
Lingayats
Vokkaliga
Must Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/karnataka-bill-to-hike-quota
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved