
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.news9live.com/viral-news/mount-etna-smoke-rings-rare-phenomenon-see-viral-videos-and-pics-2493071
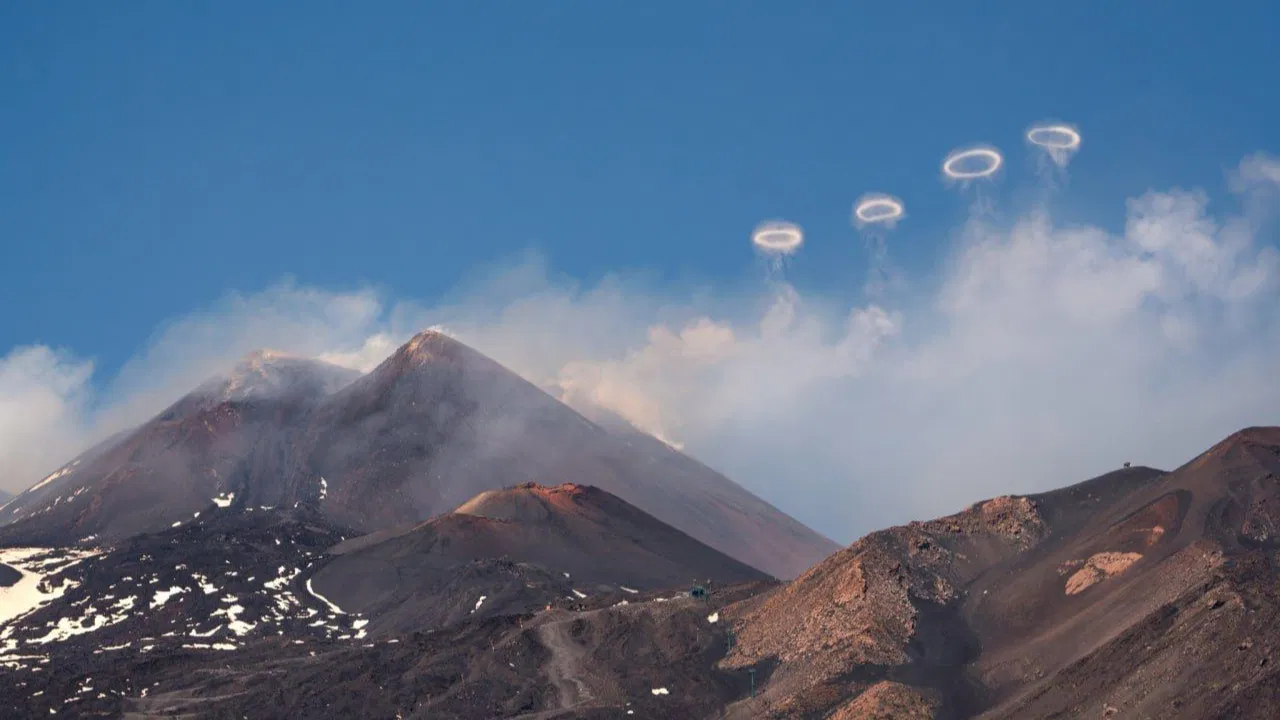
Context: Mount Etna is currently emitting volcanic vortex rings from a new vent on its crater's northeastern edge.
Details
- The volcanic vortex rings are formed when a small vent on Mount Etna's northwest border of the Southeast crater opens during an eruption.
- While Mount Etna is known for producing a high frequency of volcanic vortex rings, similar phenomena have been observed at other volcanoes worldwide, including Stromboli in Italy, Momotombo in Nicaragua, Eyjafjallajökul in Iceland, and Mount Redoubt in Alaska.
About Volcanic Vortex Rings
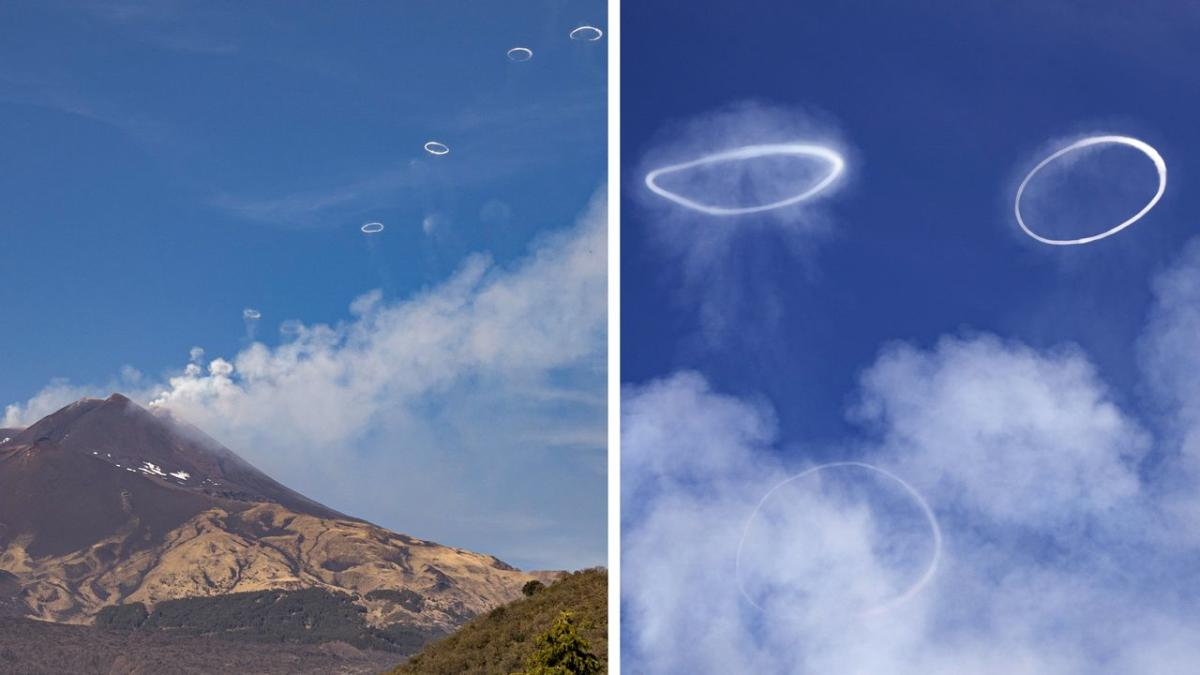
Volcanic vortex rings, also known as volcanic smoke rings, are natural phenomena associated with volcanic eruptions

Formation of Volcanic Vortex Rings
Volcanic vortex rings are formed when pressurized gases and ash are rapidly ejected from a volcanic vent during an explosive eruption. The process of ring formation can be broken down into several key steps:
- Eruption Dynamics:
- Volcanic eruptions occur when molten rock (magma), gases, and solid particles are expelled from beneath the Earth's surface.
- During explosive eruptions, pressure builds up rapidly within the volcanic conduit, leading to a sudden release of gases and volcanic ash into the atmosphere.
- Formation of the Ring:
- As the pressurised mixture of gases, ash, and volcanic particles is ejected from the vent, it interacts with the surrounding air.
- The rapid expansion of the gases and the entrainment of air around the eruptive column lead to the formation of a spinning, toroidal vortex ring.
- Vortex Dynamics:
- The spinning motion of the volcanic gases and ash generates a rotating column of air that maintains a circular shape due to the principles of fluid dynamics.
- This rotating column of gases forms a low-pressure region at its centre, contributing to the stability and persistence of the ring structure.
Key Characteristics
Size and Visibility
- Volcanic vortex rings can vary significantly in size, ranging from several metres to hundreds of metres in diameter.
- Larger and more powerful eruptions tend to produce larger and more prominent vortex rings that are visible from a considerable distance.
Appearance
- The rings appear as dense, circular bands of gas and ash that maintain their distinct shape as they rise into the atmosphere.
- They often exhibit visible vortices or swirling patterns within the ring, resembling smoke rings or vortex structures.
Factors Influencing Formation
Eruption Type
- Volcanic vortex rings are typically associated with explosive eruptions, characterised by rapid ejection of gases and volcanic material.
- The intensity, duration, and composition of the eruption influence the size and behaviour of the vortex rings.
Atmospheric Conditions
- Atmospheric factors such as wind patterns, air density, and temperature gradients can affect the stability and visibility of volcanic vortex rings.
- Calm weather conditions and minimal atmospheric disturbances enhance the visibility and longevity of these phenomena.
Scientific Significance
Insights into Volcanic Processes
- Studying volcanic vortex rings provides valuable insights into the dynamics of volcanic eruptions, including the behaviour of eruptive plumes and the dispersion of volcanic ash.
- Observations of these phenomena contribute to the development of models and simulations that improve our understanding of volcanic processes.
Public Interest and Education
- Volcanic vortex rings capture public interest due to their striking appearance and association with volcanic activity.
- They serve as educational tools for explaining volcanic phenomena and promoting awareness of volcanic hazards.
|
Volcanic vortex rings have been observed and documented during eruptions of Mount Etna in Italy, a highly active volcano known for its frequent explosive activity.
|
Conclusion
- Volcanic vortex rings are captivating natural phenomena produced during explosive volcanic eruptions, characterised by the formation of large, circular structures of gas and ash. These rings provide valuable insights into the dynamics of volcanic eruptions and contribute to our understanding of volcanic processes and their impact on the Earth's atmosphere. Studying volcanic vortex rings helps improve hazard assessments and public awareness regarding volcanic activity.
Source:
Indian Express
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which factor contributes to the longevity and travel distance of volcanic vortex rings?
A) Increased atmospheric humidity
B) Lower air pressure at higher altitudes
C) Enhanced angular momentum imparted by volcanic explosions
D) Coriolis effect due to Earth's rotation
Answer: C
|






