Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
About
Note: A typical white dwarf is half the size of our Sun and has a surface gravity 100,000 times that of Earth. Using the Hubble Space telescope and Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), astronomers have identified several white dwarfs over the years.
Composition
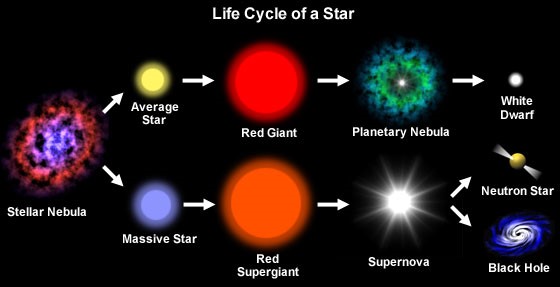
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-white-dwarf-switch-on-and-off-7587606/
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved