Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
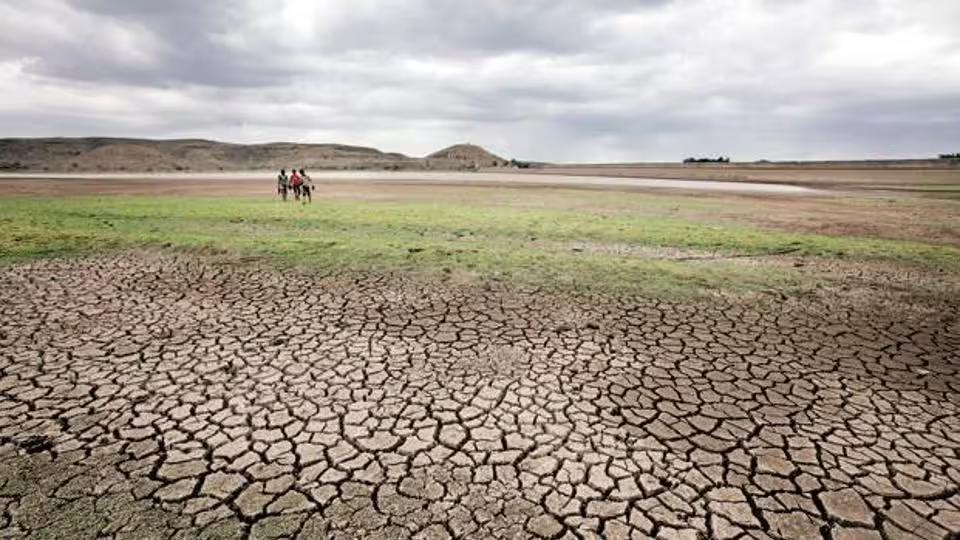
Context: India is facing a severe water crisis, facing floods and droughts at the same time.
Details
Monsoonal Climate and Variability
Topography and Geographical Factors
Climate Change and Extreme Events
|
Encroachment and Degradation of Waterbodies ●Land Encroachment: The encroachment of waterbodies for urban development, agriculture, and infrastructure reduces natural water storage capacity. This encroachment exacerbates flood risks by limiting the natural absorption of excess rainfall. Moreover, it reduces available water during droughts, as these areas would have otherwise contributed to groundwater recharge. ●Wetland Destruction: The destruction of wetlands further contributes to the loss of natural water storage and filtration systems. Wetlands play a crucial role in flood control and groundwater recharge by absorbing excess water during heavy rainfall. Their destruction disrupts these natural processes, leading to increased flood risks and reduced water availability during dry periods. |
Water Management Policies
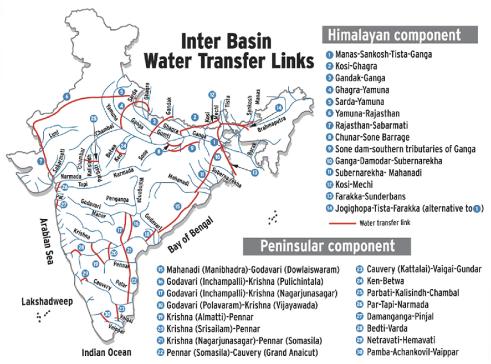
Interlinking Rivers
Community-Based Water Management
Policy Reforms and Implementation
Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM)
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The burdens of drought and flood often fall disproportionately on marginalised communities. How can India's water management strategies ensure equitable access to water resources and promote sustainable agricultural practices that are resilient to both extremes? |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved