Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/world-tb-day/
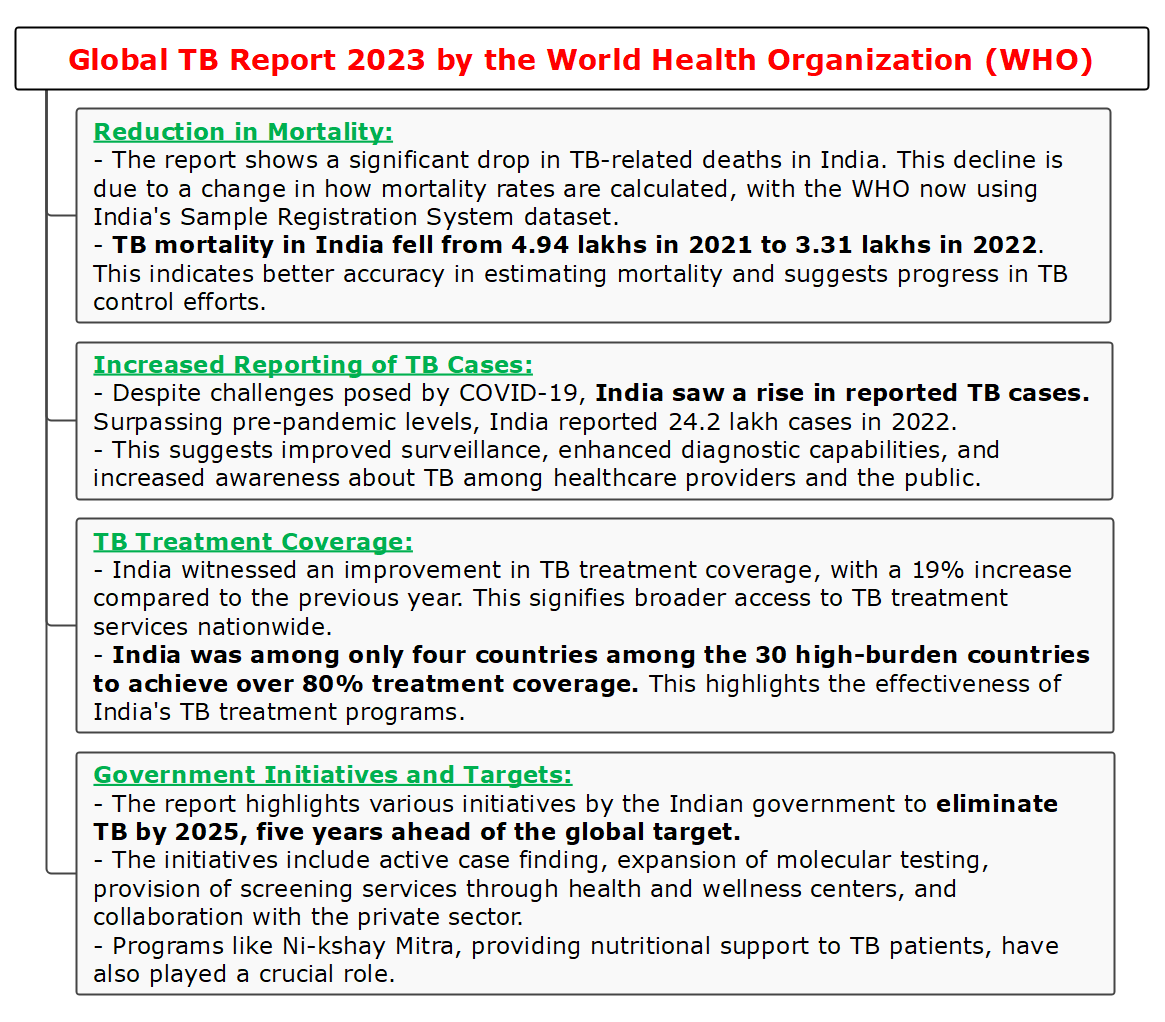
Context: World Tuberculosis (TB) Day is celebrated every year on 24th March to promote awareness about tuberculosis, a deadly infectious disease that mainly affects the lungs.
World Tuberculosis Day 2024
Tuberculosis
Symptoms
Transmission
Diagnosis
Prevention
Treatment
Must Read Articles:
TUBERCULOSIS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/tuberculosis
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What is the primary mode of transmission for tuberculosis? A) Foodborne B) Sexual contact C) Airborne D) Waterborne Answer: C |
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved