Prime Minister Awas Yojana – Various Aspects of the scheme

Context
- Discussion on various aspects of the Prime Minister Awas Yojana.
Key Details:
- The Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra is being organized in 6 thousand 7 Hundred 94 gram panchayats of 30 districts in Odisha.
- Awareness about the public welfare schemes of the central government is being spread among the people under this program in 283 cities.
- The program covers schemes like PM Awas Yojana (Gramin), National Rural Livelihood Mission, PM Kisan, Crop Insurance Scheme, Poshan Abhiyan, Ujjwala Yojana, Ayushman Bharat, Janaushadhi Yojana, PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana.
- In addition to organizing health camps, arrangements have also been made for the registration of the beneficiaries under various schemes.
- According to sources, the Ministry of Rural Development, which is in charge of the PMAY-G scheme, has decided to reassign 1.44 lakh houses under the PMAY-G scheme from 23 states and UTs to Uttar Pradesh, as these states and Union Territories (UTs) could not sanction the houses by the deadline of June 30.
- The PMAY-G scheme aims to build 2.95 crore houses for the rural poor by March 2024, before the next general elections.
- The Ministry of Rural Development, which oversees the scheme, has informed the states and UTs about the revised allocation of houses under the rural housing scheme.
- The states and UTs that have lost their allocation are Gujarat, Tripura, Odisha, Sikkim, Meghalaya, Maharashtra, Assam, Nagaland, Mizoram, Tamil Nadu, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Ladakh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Jharkhand, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand and Andhra Pradesh.
What is Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana?
| In the Budget 2023, the outlay for the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana was enhanced by 66% to over Rs.79,000 crore. |
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana is a social welfare flagship program of the Indian Government. It was launched by our honorable Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi in 2015.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) was launched to provide housing at an affordable price to the weaker sections of society, lower income groups people, the urban poor, and the rural poor.
- The Yojana involves the construction of around 20 million houses at an affordable price. In the Budget 2023, the outlay for the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana was enhanced by 66% to over Rs.79,000 crore.
The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana has two components:
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G)
- PMAY-G is a flagship scheme of the central government that aims to provide affordable housing to the rural poor. The scheme was launched in 2016 as a successor to the Indira Awaas Yojana (IAY).
- Under PMAY-G, beneficiaries are identified through the Socio-Economic and Caste Census (SECC) data and are provided assistance of Rs 1.2 lakh in plain areas and Rs 1.3 lakh in hilly areas for constructing a pucca house with basic amenities.
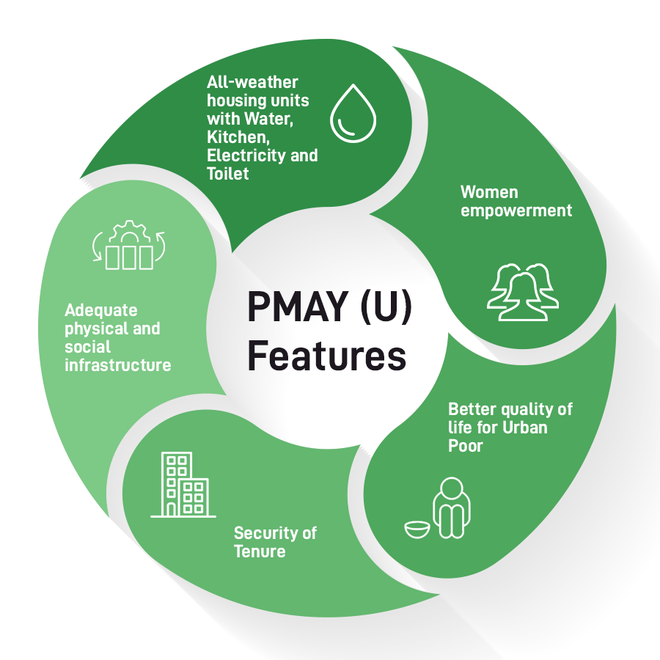
Features
- The scheme is demand-driven and beneficiary-led, meaning that the beneficiaries have a say in the design, location, and construction of their house.
- It uses geo-tagging and Aadhaar-linked paymentsto ensure transparency and accountability in the implementation process.
- It promotes convergence with other schemessuch as Swachh Bharat Mission, MGNREGA, Ujjwala Yojana, etc. to provide additional benefits to the beneficiaries.
- It encourages the use of local materials and technologiesto reduce the cost and environmental impact of construction.
- It provides technical support and trainingto the beneficiaries and masons to improve the quality and durability of the houses.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban) Programme

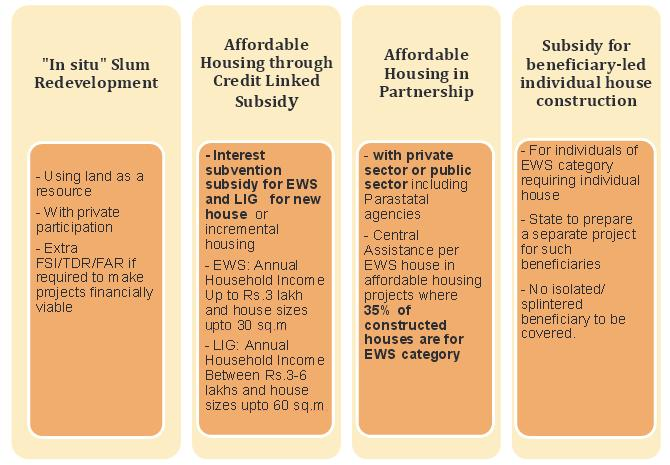
- In Situ Slum Redevelopment: A slum rehabilitation grant of Rs. 1 lakh per house, on average, would be admissible for all houses built for eligible slum dwellers in all such projects. Slums so redeveloped should compulsorily be denotified.
- Affordable Housing through Credit Linked Subsidy: Under Credit Linked Subsidy, beneficiaries of the Economically Weaker Section (EWS) and Low-Income Group (LIG) can seek housing loans from Banks, Housing Finance Companies, and other such institutions for new construction and enhancement of existing dwellings as incremental housing.
- Affordable Rental Housing Complexes: It will be a mix of single/double bedroom Dwelling Units and a Dormitory of 4/6 beds including all common facilities which will be exclusively used for rental housing for a minimum period of 25 years.
The scheme is also linked with other schemes like:
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan which aims at reducing open defecation by constructing in-house toilets and community-owned toilets and aims to maintain cleanliness around the streets, roads, and houses
- Saubhagya Yojana which aims at providing electricity connection
- Ujjwala Yojana which aims to provide LPG Gas connection
- Accessibility of pure drinking water
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana which aims at opening a zero balance account and spreading banking facilities to every person in the society.
Components of PM Awas Yojana:
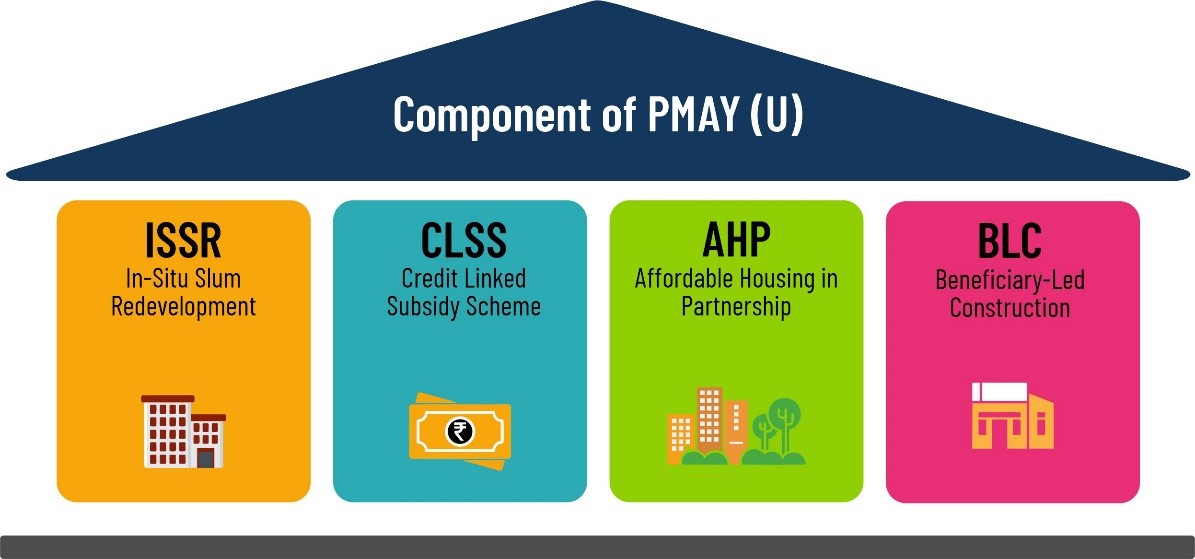
The PM Awas Yojana has 4 major components:
- In-situ redevelopment of slums using land as a resource, with the participation of the private sector. This mission aims at leveraging the potential of land under slum areas and providing formal urban establishments to slum dwellers.
Credit Linked Subsidy –
- Under this scheme, the government will provide an interest subsidy of 6.5% on housing loans for 15 years from the start of the loan, which will make housing affordable.
- The Net Present Value (NPV) of the interest subsidy will be calculated at a discount rate of 9%. The loan amount of Rs 6 lakhs is only applicable for the credit-linked subsidy scheme and any amount beyond Rs 6 lakh does not attract any subsidy.
- The lending institutions will directly credit the interest subsidy to the beneficiaries’ accounts which will result in reduced Equated Monthly Installment (EMI) and reduced housing loan amount.
Affordable Housing in Partnership (AHP) –
- In partnership with the Public and Private sectors, affordable housing will be provided to the economically weaker sections.
- The States or Union Territories, either with different agencies or in partnership with different industries can plan affordable housing projects.
Enhancement and construction of a beneficiary-led house –
- Under this component, the beneficiaries who are not able to avail the advantages of the above three components will benefit.
- This mission assists families of the EWS category to construct new houses or enhance the existing houses on their own to cover the beneficiaries.
- Under this mission, families will get central assistance of Rs 1.50 lakh to enhance their existing houses or construct new houses.
- Under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, the houses will be constructed with eco-friendly technology and preference will be given to old and disabled while allotting ground floors.
Significances:
- It addresses the housing deficit and homelessness among the rural poor, which is a basic human right and a prerequisite for dignity and social inclusion.
- It promotes rural employment and livelihoods by creating demand for local materials and labor in the construction sector.
- It improves the health and hygiene of the rural population by providing sanitation facilities and clean cooking fuel along with the houses.
- It reduces the vulnerability of the rural poor to natural disasters and climate change by ensuring disaster-resilient and energy-efficient houses.
- It contributes to the overall economic growth and social development of the country by reducing poverty and inequality.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of affordable housing units under PMAY contributes to the overall development of infrastructure in both urban and rural areas, enhancing the quality of life for residents.
- Economic Growth: The scheme stimulates economic growth by generating employment opportunities in the construction sector. It also has a cascading effect on various related industries, contributing to the country's overall economic development.
- Improved Living Conditions: By providing affordable and quality housing, PMAY improves the living conditions of the beneficiaries. This, in turn, has positive effects on health, education, and overall well-being.
- Rural-Urban Linkages: PMAY addresses housing needs in rural and urban areas, bridging the gap and creating a more balanced approach to development.
- Women Empowerment: The scheme emphasizes the role of women as co-applicants, ensuring that women have equal ownership rights in the allocated houses. This contributes to women's empowerment and gender equality.
What are the challenges of PMAY?
- Delayed release of funds: The central and state governments often delay the release of funds to the beneficiaries, which affects their ability to start or complete the construction work on time.
- Inadequate verification: The verification of beneficiaries based on the SECC data is often inadequate or faulty, leading to the exclusion of eligible households or the inclusion of ineligible ones.
- Poor quality: The quality of construction is often compromised due to a lack of skilled labor, technical guidance, quality control, and supervision.
- Corruption: There are instances of corruption and misappropriation of funds at various levels of implementation, such as diversion of funds, fake beneficiaries, inflated bills, and substandard materials.
- Lack of awareness: Many beneficiaries are unaware of their entitlements, rights, and responsibilities under the scheme. They also lack information on the design options, construction techniques, and maintenance practices.
- Land Availability: Acquiring suitable land for housing projects, especially in urban areas, can be a major hurdle. The scarcity of land and its rising costs can impede the progress of constructing affordable housing.
- Infrastructure Development: Creating the necessary infrastructure like roads, water supply, and sanitation facilities in the designated areas for housing can be a time-consuming process. Lack of proper infrastructure can affect the quality of life for residents.
- Technology Adoption: The successful implementation of PMAY also depends on the effective use of technology for project monitoring, beneficiary identification, and other administrative tasks. Ensuring that the technology is accessible and utilized optimally can be a challenge.
- Quality Control: Maintaining the quality of construction and ensuring that the housing units are habitable and durable is a constant challenge. Stringent quality control measures are necessary to prevent substandard construction.
Possible Steps that can be taken are:
- Streamlining the fund flow mechanism: The central and state governments should ensure the timely and adequate release of funds to the beneficiaries through direct benefit transfer (DBT) or other transparent modes.
- Strengthening the verification process: The verification of beneficiaries should be done through multiple sources such as Aadhaar, bank accounts, gram sabha resolutions, and geo-tagging.
- Improving the quality standards: The quality standards should be strictly enforced through regular inspections, audits, and feedback mechanisms. The beneficiaries should also be trained and sensitized on quality aspects.
- Curbing corruption: Corruption cases should be promptly investigated and penalized. The grievance redressal mechanism should be made more accessible and responsive.
- Enhancing awareness: The awareness campaigns should be intensified and diversified through various media such as print, electronic, social media, and folk art. The beneficiaries should also be involved in participatory planning and monitoring of the scheme.
Closing thoughts
- PMAY stands as a commendable effort towards fulfilling the housing needs of the Indian population. It serves as a model for inclusive and sustainable urban and rural development, although ongoing efforts are essential to address challenges and ensure its continued success.
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.zeebiz.com%2Findia%2Freal-estate%2Fnews-union-cabinet-extends-pradhan-mantri-awas-yojana-gramin-scheme-approves-rs-217257-crore-for-scheme-172864&psig=AOvVaw2quzIpM0x9oWCmaPjC9Fv8&ust=1701967904677000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=2ahUKEwiV_KTUovuCAxVrSmwGHV6JDOIQr4kDegQIARBX
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.youtube.com%2Fwatch%3Fv%3DytaInJ40rIQ&psig=AOvVaw2quzIpM0x9oWCmaPjC9Fv8&ust=1701967904677000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=2ahUKEwiV_KTUovuCAxVrSmwGHV6JDOIQr4kDegQIARBJ
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.businessleague.in%2Fpm-awas-yojana-new-facility-good-news-now-you-will-get-these-four-facilities-with-home-know-details-here%2F&psig=AOvVaw2C-At5l__DtrRSg1qEwbln&ust=1701968036565000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=2ahUKEwim4ZaTo_uCAxX2Q2cHHeEoDzEQr4kDegQIARA3
https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fnewsonair.gov.in%2FNews%3Ftitle%3DYear-Ender-2020%253A-Report-on-Pradhan-Mantri-Awas-Yojana-%2528Gramin%2529%26id%3D406619&psig=AOvVaw2C-At5l__DtrRSg1qEwbln&ust=1701968036565000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=2ahUKEwim4ZaTo_uCAxX2Q2cHHeEoDzEQr4kDegQIARA9

Jammu and Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023
Context
- The Lok Sabha on Wednesday (6th December 2023) passed the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023, and the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
Key features of the bill:
- The Jammu and Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023, amends the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004.
- The Act provides reservation in jobs and admission in professional institutions to members of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and other socially and educationally backward classes.
- On the other hand, the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023 amends the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019.
- The 2019 Act amended the Second Schedule of the 1950 Act to specify the total number of seats in the Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly to be 83.
- The proposed Bill increases the total number of seats to 90. It also reserves seven seats for Scheduled Castes and nine seats for Scheduled Tribes.
- The Bill adds that the Lieutenant Governor may nominate up to two members from the Kashmiri migrant community to the Legislative Assembly.
- One of the nominated members must be a woman. Migrants are defined as persons who migrated from the Kashmir Valley or any other part of the state of Jammu and Kashmir after 1st November 1989 and are registered with the Relief Commissioner.
Significance and Intentions:
- The reservation of seats for Kashmiri Pandits and migrants from PoK is aimed at addressing the concerns of these communities who have faced displacement and challenges due to the region's political history and conflicts. It intends to give them a voice and representation in the democratic processes of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The provision to empower the L-G to nominate these MLAs is likely to ensure their representation in the Legislative Assembly, especially in situations where holding regular elections in certain areas may be challenging due to security or other considerations.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Lok-Sabha-passes-Jammu-and-Kashmir-Reservation-and-Reorganisation-Amendment-Bills&id=472607
.jpg)
India and Papua New Guinea
Context
- India has announced immediate relief assistance of one million dollars to Papua New Guinea after a volcanic eruption.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- On 20th November, a major volcanic eruption of Mount Ulawun in Papua New Guinea forced the evacuation of more than 26 thousand people and created urgent humanitarian needs.
- New Delhi has extended immediate relief assistance to support relief, rehabilitation, and reconstruction efforts in the country, as a close friend and development partner under the Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation.
- The External Affairs Ministry said in a release that India has extended sympathy to the Government and the people of Papua New Guinea for the damage and destruction caused by the disaster.
About Papua New Guinea:
- New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2.
- Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf.
- Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east.
- Mount Ulawun is an impressive stratovolcano located in Papua New Guinea. Standing at 2,334 meters (7,657 feet) above sea level, it is one of the highest and most active volcanoes in the country.
- Ulawun is situated on the island of New Britain and dominates the landscape with its conical shape.
- This volcano is known for its frequent eruptions, with the first recorded eruption dating back to 1700. Since then, it has erupted multiple times, with significant events occurring in the 20th and 21st centuries.
- The eruptions are often characterized by lava flows, ash emissions, and pyroclastic flows.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-to-provide-immediate-relief-assistance-of-one-million-dollars-to-Papua-New-Guinea-in-wake-of-volcanic-eruption&id=472621

Garba of Gujarat inscribed in UNESCO's List
Context
- Garba of Gujarat has been inscribed in the Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) of Humanity by UNESCO.

Details
- This decision has been taken at the Botswana convention of UNESCO on Wednesday (6th December 2023).
- Union Minister G. Kishan Reddy in a social media post, said that this listing is testimony to the tireless efforts of the government under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi to showcase our rich culture, traditions, and heritage to the world.
- AIR correspondent reports, Garba of Gujarat is the 15th ICH element from India to join this list. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Intangible Cultural Heritage is underway in Botswana.
- The live screening of the same is arranged by the Gujarat government in all the districts of the State. Special cultural programs along with traditional garba will be organized at four iconic locations along with live streaming in the state.
About the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Intangible Cultural Heritage:
|
About
|
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) Intangible Cultural Heritage refers to the cultural elements that are not physical but are nonetheless considered valuable and worthy of preservation.
- Unlike tangible cultural heritage, which includes physical artifacts such as buildings, monuments, and artifacts, intangible cultural heritage encompasses traditions, oral expressions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, knowledge, and skills passed down from generation to generation.
|
Key features of UNESCO's Intangible Cultural Heritage include:
- Diversity: Intangible cultural heritage reflects the rich diversity of human expressions and ways of life. It includes a wide range of practices and knowledge that contribute to the identity and continuity of communities around the world.
- Community-Based: UNESCO emphasizes the importance of involving communities, groups, and individuals who are the bearers of intangible cultural heritage in its identification, safeguarding, and transmission. The active participation of these stakeholders is crucial for the preservation and sustainability of these cultural elements.
- Safeguarding: UNESCO encourages the safeguarding of intangible cultural heritage to ensure its viability and transmission to future generations. This involves various measures, including documentation, research, promotion, education, and the revitalization of endangered practices.
- Lists: UNESCO maintains two main lists related to intangible cultural heritage: the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity and the List of Intangible Cultural Heritage in Need of Urgent Safeguarding. The Representative List aims to showcase the diversity of intangible heritage worldwide, while the Urgent Safeguarding List focuses on elements that require immediate attention to prevent their disappearance.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Garba-of-Gujarat-inscribed-in-UNESCO%26%2339%3bs-List-of-Intangible-Cultural-Heritage-of-Humanity&id=472610

Combined Leadership Conclave
Context
- Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan on Wednesday (6th December 2023) presided over the first session of the Combined Leadership Conclave in New Delhi.

Details:
- In a statement, the Defence Ministry said that CDS provided an insight into modern warfare and national security during the session.
- The three-day conclave focuses on geo-strategic issues, national security, defense, and emerging security challenges as well as self-reliance in defense.
- The conclave also aims to serve as a development program for senior officers of the three services, focused on regional and national security issues.
About the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS):
|
About
|
- The Chief of Defence Staff India position was established to enhance tri-service effectiveness, coordination, and overall integration of the Indian armed forces' combat capabilities.
- The government changed the Army, Navy, and Air Force service rules to make retired Service Chiefs and three-star officers eligible for consideration for the nation's top military position. The retired officer's age should not have exceeded 62 years at the time of appointment.
- A Group of Ministers (GoM) entrusted with analyzing the Kargil Review Committee (1999) report suggested its creation in 2001.
|
|
Roles and responsibilities
|
- Single Military Advisor: The CDS serves as the principal military advisor to the Defense Minister on all matters concerning the three branches of the Indian armed forces—Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Inter-Service Harmony: The primary duty of the CDS is to ensure a high level of inter-service harmony. This involves fostering cooperation and coordination among the different services to achieve a unified and synergized approach to military operations.
- Operational Synergy: The CDS is responsible for promoting stronger operational synergy among the three service components. This includes strategic planning, joint training, and coordination in military operations to enhance overall effectiveness.
- Procurement Decision Authority: As the chairman of the Permanent Chairman-Chiefs of Staff Committee, the CDS has the authority to determine the order of importance for inter-service procurement decisions. This helps in prioritizing and optimizing the allocation of resources for defense acquisitions.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Chief-of-Defence-Staff-presides-over-first-session-of-Combined-Leadership-Conclave-in-New-Delhi&id=472614











