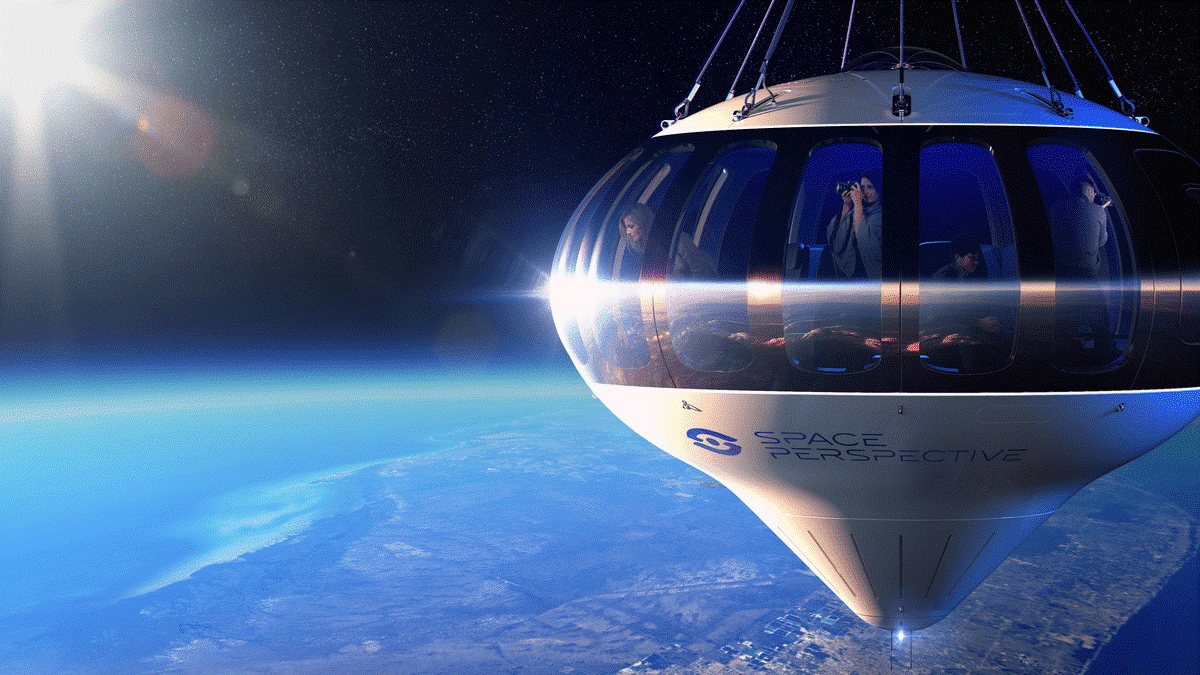
SPACE TOURISM
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The Government is taking measures to augment domestic capacity for the future realisation of space tourism- said Atomic Energy and Space Minister Dr Jitendra Singh.
What is Space Tourism?
- Space tourism is a branch of space exploration that enables ordinary individuals to visit space for leisure, economic, or recreational purposes. There are several different types of space tourism, including orbital, suborbital and lunar space tourism.
|
Orbital Space Travel means the spacecraft is traveling around the planet with enough speed to avoid falling back to Earth. The International Space Station (ISS) is an example of orbital space travel.
Suborbital Space Travel takes people into space and then returns to Earth at a slower speed than orbital travel.
|
Note: Experts disagree over exactly how far space is from the Earth. While many international organizations consider the Kármán line—which is 60 miles high—to be the edge of the Earth’s atmosphere, the Federal Aviation Administration and NASA define everything above 50 miles to be “outer space.”
A brief History of Space Tourism:
- The first space traveller was US businessman Dennis Tito, who spent 8 days aboard the International Space Station in 2001.
- Between 2001 to 2009, seven space tourists made eight space flights aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraftto the International Space Station. But Russia halted orbital space tourism in 2010 due to the increase in the International Space Station crew size.
- Russian orbital tourism eventually resumed with the launch of Soyuz MS-20in 2021.
- In 2019, NASAannounced that it aims to start allowing private astronauts to go on the International Space Station, with the use of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Work also continues towards developing suborbital space tourism vehicles.
- Today, SpaceX founded by Elon Musk is leading in the space tourism market and is taking tourists in its Dragon capsule (which was lifted by the Falcon 9 rocket) on flights in zero gravity.
Pros and cons of Space Tourism:
Cons
- It’s expensive: At hundreds of thousands of dollars per ticket, only the wealthiest travelers can afford a seat on a future spaceflight.
- Bad for the environment: Scientists worry that space travel could damage the planet and contribute to climate change. Carbon released by 1,000 private suborbital flights per year would increase the temperature over the poles by 1 degree Celsius and reduce polar sea ice levels by 5% each year.
- Exposure to Sun’s Radiation: Space travellers are likely to get exposed to harmful radiations from the sun.
- Health: Spending long hours in zero gravity condition can be dangerous for the person’s cardiovascular and musculoskeletal system. If people accidentally get exposed to high-energy ionizing cosmic rays, it may lead to cancer. Space travel can make passengers queasy and disoriented, which can impair their vision, cognition, balance, and motor skills.
- Exposure to harmful organisms: It can introduce some harmful microorganism from space into the atmosphere of Earth.
- Poor Regulation: Lack of proper regulation and inadequate safety protocols can make space travel extremely dangerous.
- Commercialization: Companies engaged in this may fail to stick to safety measures in a spree to gather more customers.
- Waste of Resources: Experimentation and unsuccessful ventures may cause an unnecessary waste of resources.
- Could alleviate poverty rather: Developing spacecrafts need a lot of money. That money can be utilized for alleviation of poverty.
- Inequity: It is meant for the super-rich only. A single 2 ½ hour flight ticket in Virgin Galactic’s upcoming space ship costs $ 250,000.
- Not a panacea: It would not be wise to consider the escape to space will help in escaping the problems of earth. There is nowhere in the solar system where we can find the environment as congenial as that available on earth.
Pros
- Boost to Economy: Space tourism has the potential to boost the economy by creating jobs and encouraging investment.
- Advances in research: Spending more time in space could help solve some of the most baffling mysteries about the universe.
- Opportunity to experience space: It will enable more people than ever before to go to space to gaze into the unknown and imagine what could be, and to look down at Earth and gain a new perspective on home.
- Generate Employment: Space tourism will give employment to thousands of people. Manufacturing of new and better spacecraft will give employment to many skilled people.
- Draw Investors: It will renew interest in space exploration. This will draw more investors for more financial backing to support more innovations in the industry.
- Pave ways to protect Earth: It would also help in identifying potential hazards dangerous for our planet.
- Technological Advancement: Opens avenues for advanced technology which can be applied to other domains apart from space missions.
- New Resources: It will help in finding new minerals and other precious materials in space and other planets. This is of great significance for people of Earth where natural resources are depleting fast.
- Adventure Tourism: Open a new avenue for adventure tourists.
- Innovation and Exploration: Space tourism programs can encourage further innovation and exploration of our solar system and beyond. Taking more people into space creates opportunities to invent new space technology, conduct ground-breaking research and establish new frontiers in galaxies beyond our own.
Future Potential:
- The space tourism market has boomed in recent years, with commercial aerospace companies dominating it.
- By 2040, the industry is expected to have grown from $350 million in 2019 to more than $1 trillion.
Space Tourism in India:
- The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe) seeks to promote active participation of the private sector in carrying out end-to-end space activities, which includes space tourism as well. IN-SPACe will come up with mechanisms to enable sharing of technical facilities and expertise available across ISRO Centres with private entities.
- ISRO has already carried out a few feasibility studies for a sub-orbital space tourism mission onboard a liquid propellant stage booster. Through Gaganyaan - India’s maiden human spaceflight programme - ISRO is engaged in the development of various technologies, which are essential building blocks for human space missions.
- Need of the hour: Develop and successfully test reusable rockets meant for ferrying tourists. During the tests it should be reliable and low cost and should be feasible enough.
- The goal is for scientists and engineers to find a way to drive down costs enough to make ‘space tourism’ a viable industry.
Citations:
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Govt-is-taking-measures-to-augment-domestic-capacity-for-the-future-realisation-of-space-tourism%3a-Dr-Jitendra-Singh&id=455111
https://www.rd.com/article/space-tourism/
https://www.financialexpress.com/lifestyle/science/space-tourism-in-india-get-ready-it-might-become-reality-soon/2605862/
https://www.indiatoday.in/science/story/isro-developing-capability-to-launch-humans-on-quick-space-tourism-flights-1978221-2022-07-21
.jpeg)
LIGHT COMBAT AIRCRAFT TEJAS

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The indigenous Light Combat Aircraft Tejas will hold a centre stage of India Pavilion at the 14th edition of Aero India show.
LCA Tejas and its Features:
- LCA Tejas is a 4.5 generation, all weather and multi-role fighter aircraft.
- Tejas is a highly agile, multi-role supersonic fighter designed for air combat, and offensive air support with reconnaissance and anti-ship capabilities.
- The aircraft is capable of taking up offensive air support, close combat and ground attack role at ease. It is also designed to undertake Ground Maritime Operations.
- Tejas is fully capable of carrying a load of eight to nine tonnes.
- Its biggest advantage is its speed. These aircraft can fly as fast as the speed of sound, i.e., Mach 1.6 to 1.8, up at an altitude of 52,000 feet. The Tejas currently has three production models – Tejas Mark 1, Mark 1A and trainer.
- Tejas is fitted with an active electronically-scanned radar for critical operation capability. It can refuel in the air and be ready for war again. It can target enemy aircraft from a distance. It also has the ability to dodge the enemy's radar.
Note: Tejas made its first flight in January 2001. The aircraft was inducted into the squadron of the Indian Air Force in 2016.
Aero India Show
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=LCA-Tejas-to-be-at-the-centre-stage-of-%e2%80%98India-Pavilion%e2%80%99-at-14th-edition-of-Aero-India-Show&id=455103

WORLD WETLANDS DAY

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- World Wetlands Day is celebrated every year on 2nd
Aim:
- To create awareness about conservation, significance and the role of wetlands in the protection of biodiversity.
World Wetlands Day 2023 Theme:
- The theme of World Wetlands Day 2023 is “It's Time for Wetlands Restoration”.
- The theme emphasises the urgent need to prioritise wetland restoration.
Wetlands in India:
- With 75 Ramsar sites covering over 13 lakh Hectares, India has the largest number of Wetlands in South Asia.
- Being the leader in the region in terms of number of Wetlands, India assumes prominence in sending a global message on conservation of one of the important ecosystems.
Read about Wetlands: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/wetlands
Read about Ramsar Convention: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/ramsar-convention
Updated List of Ramsar Sites in India
|
Ramsar Site
|
State
|
Designated Year
|
Area (km2)
|
|
1
|
Kolleru Lake
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
2002
|
901
|
|
2
|
Deepor Beel
|
Assam
|
2002
|
40
|
|
3
|
Kanwar (Kabar) Taal
|
Bihar
|
2020
|
26.2
|
|
4
|
Nanda Lake
|
Goa
|
2022
|
0.42
|
|
5
|
Khijadia WLS
|
Gujarat
|
2021
|
6
|
|
6
|
Nalsarovar BS
|
Gujarat
|
2012
|
123
|
|
7
|
Thol Lake
|
Gujarat
|
2021
|
6.99
|
|
8
|
Wadhvana Wetland
|
Gujarat
|
2021
|
10.38
|
|
9
|
Bhindawas WLS
|
Haryana
|
2021
|
4.11
|
|
10
|
Sultanpur NP
|
Haryana
|
2021
|
142.5
|
|
11
|
Chandra Taal
|
Himachal Pradesh
|
2005
|
0.49
|
|
12
|
Pong Dam Lake
|
Himachal Pradesh
|
2002
|
156.62
|
|
13
|
Renuka Lake
|
Himachal Pradesh
|
2005
|
0.2
|
|
14
|
Ranganathituu BS
|
Karnataka
|
2022
|
5.18
|
|
15
|
Ashtamudi Wetland
|
Kerala
|
2002
|
614
|
|
16
|
Sasthamkotta Lake
|
Kerala
|
2002
|
3.73
|
|
17
|
Vembanad-Kol Wetland (Longest Lake in India)
|
Kerala
|
1905
|
1512.5
|
|
18
|
Bhoj Wetland
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
2002
|
32
|
|
19
|
Sakhya Sagar
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
2022
|
2.48
|
|
20
|
Sirpur wetland
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
2022
|
1.61
|
|
21
|
Yashwant Sagar
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
2022
|
8.22
|
|
22
|
Lonar Lake (Impact Crater Lake)
|
Maharashtra
|
2020
|
4.27
|
|
23
|
Nandur Madhameshwar
|
Maharashtra
|
2019
|
14
|
|
24
|
Thane Creek
|
Maharashtra
|
2022
|
65.21
|
|
25
|
Loktak Lake
|
Manipur
|
1990
|
266
|
|
26
|
Pala Wetland
|
Mizoram
|
2021
|
18.5
|
|
27
|
Ansupa Lake
|
Odisha
|
2021
|
2.31
|
|
28
|
Bhitarkanika Mangroves
|
Odisha
|
2002
|
650
|
|
29
|
Chilika Lake (Oldest Ramsar Site in India)
|
Odisha
|
1981
|
1165
|
|
30
|
Hirakud Reservoir
|
Odisha
|
2021
|
654
|
|
31
|
Satkosia Gorge
|
Odisha
|
2021
|
981.97
|
|
32
|
Tampara Lake
|
Odisha
|
2021
|
3
|
|
33
|
Beas CnR
|
Punjab
|
2019
|
64
|
|
34
|
Harike Wetland
|
Punjab
|
1990
|
41
|
|
35
|
Kanjli Wetland
|
Punjab
|
2002
|
1.83
|
|
36
|
Keshopur-Miani CmR
|
Punjab
|
2019
|
34
|
|
37
|
Nangal WLS
|
Punjab
|
2019
|
1
|
|
38
|
Ropar Wetland
|
Punjab
|
2002
|
13.65
|
|
39
|
Keoladeo National Park
|
Rajasthan
|
1981
|
28.73
|
|
40
|
Sambhar Lake
|
Rajasthan
|
1990
|
240
|
|
41
|
Chitrangudi BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2021
|
2.6
|
|
42
|
Gulf of Mannar Marine BR
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
526.72
|
|
43
|
Kanjirankulam BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.96
|
|
44
|
Karikili BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.584
|
|
45
|
Koonthankulam BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2021
|
0.72
|
|
46
|
Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
12.475
|
|
47
|
Pichavaram Mangrove
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
14.786
|
|
48
|
Point Calimere WLS & BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2002
|
385
|
|
49
|
Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.94
|
|
50
|
Udhayamarthandapuram BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.44
|
|
51
|
Vaduvur BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
1.12
|
|
52
|
Vedanthangal BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.4
|
|
53
|
Vellode BS
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.77
|
|
54
|
Vembannur Wetland Complex
|
Tamil Nadu
|
2022
|
0.2
|
|
55
|
Rudrasagar Lake
|
Tripura
|
2005
|
2.4
|
|
56
|
Hokera Wetland
|
UT of JK
|
2005
|
13.75
|
|
57
|
Hygam Wetland CnR
|
UT of JK
|
2022
|
8.02
|
|
58
|
Shallbugh Wetland CnR
|
UT of JK
|
2022
|
16.75
|
|
59
|
Surinsar-Mansar Lakes
|
UT of JK
|
2005
|
3.5
|
|
60
|
Wular Lake
|
UT of JK
|
1990
|
189
|
|
61
|
Tso Kar (High Altitude Ramsar Site)
|
UT of Ladakh
|
2020
|
95.77
|
|
62
|
Tsomoriri (High Altitude Ramsar Site)
|
UT of Ladakh
|
2002
|
120
|
|
63
|
Bakhira WLS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2021
|
28.94
|
|
64
|
Haiderpur Wetland
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2021
|
69
|
|
65
|
Nawabganj BS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
2
|
|
66
|
Parvati Arga BS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
7
|
|
67
|
Saman BS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
5
|
|
68
|
Samaspur BS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
8
|
|
69
|
Sandi BS
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
3
|
|
70
|
Sarsai Nawar Jheel
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2019
|
2
|
|
71
|
Sur Sarovar (Keetham Lake)
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2020
|
4.31
|
|
72
|
Upper Ganga River (Brijghat to Narora)
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
2005
|
265.9
|
|
73
|
Asan Barrage
|
Uttarakhand
|
2020
|
4.44
|
|
74
|
East Kolkata Wetlands
|
West Bengal
|
2002
|
125
|
|
75
|
Sundarban Wetland (Largest Ramsar Site in India)
|
West Bengal
|
2019
|
4230
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Today-is-World-Wetlands-Day&id=455086
OPEN MARKET SALE SCHEME

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The Food Corporation of India FCI has sold over eight Lakh Metric Tonnes of wheat under the Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic) on the first day of e-auction across 22 states.
Open Market Sale Scheme:
- About: Open Market Sale Scheme(OMSS) refers to selling of foodgrains by Government / Government agencies at predetermined prices in the open market from time to time.
- Aim: The aim is to enhance the supply of grains especially during the lean season and thereby to moderate the general open market prices especially in the deficit regions.
Other Features
- For transparency in operations, the Corporation has switched over to e- auction for sale under Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic).
- The Food Corporation of India conducts a weekly auction to conduct this scheme in the open market using the platform of commodity exchange NCDEX(National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Limited).
- The State Governments/ Union Territory Administrations are also allowed to participate in the e-auction, if they require wheat and rice outside Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
The present form of OMSS comprises 3 schemes as under:
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
- Sale of wheat to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction by dedicated movement.
- Sale of Raw Rice Grade ‘A’ to bulk consumers/private traders through e-auction.
|
Food Corporation of India (FCI)
The Food Corporation of India (FCI) is a statutory corporation.
It is under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, formed in Food Corporation Act, 1964.
Its top official is designated as Chairman who is a central government civil servant of the IAS cadre. It was set up in 1965.
Mandate
Effective price support operations for safeguarding the interests of the poor farmers.
Distribution of foodgrains throughout the country for Public Distribution System (PDS).
Maintaining a satisfactory level of operational and buffer stocks of food grains to ensure National Food Security.
Regulate market price to provide foodgrains to consumers at a reliable price.
|
Read: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/agri-commodities-trading
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Over-eight-Lakh-Metric-Tonnes-of-wheat-sold-by-FCI-under-Open-Market-Sale-Scheme-on-first-day-of-e-auction&id=455079
VISIT INDIA YEAR 2023 INITIATIVE
Context:
- Minister of Tourism G. Kishan Reddy launched the Visit India Year - 2023 initiative and also unveiled its logo.
Details:
- The Visit India Year 2023 campaign is an initiative of the Tourism Ministry.
- It has been launched to encourage inbound travel to the country which is currently holding the presidency of G20.
- Due to its Presidency in G-20, more than one lakh foreign delegates will visit India this year.
- So, this is an opportunity and they will be showcased the entire gamut of India's culture, including monuments and festivals under the Visit India Year 2023 campaign.
- Each foreign delegate of G20 will be a brand ambassador of India's culture, heritage and tourist destinations.

https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Tourism-minister-launches-Visit-India-Year-2023-initiative%2c-logo-in-New-Delhi&id=454989







