INDIA-FRANCE STRATEGIC PARTNERSHIP IN DEFENCE SECTOR

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to France is likely to boost economic cooperation between India and France and shape broader strategic ties between European Union and India, Media India Group reported, adding that his visit to France holds special significance as the two nations are celebrating 25 years of their strategic partnership.
Key Details:
- PM Modi’s visit presents an opportunity for the two nations to move into the next phase in the India-France strategic partnership and set new ambitious goals for cultural, scientific, academic, and economic cooperation and a wide range of interests.
- India has signed more than 35 strategic partnerships agreement with countries. However, India signed the first-ever strategic partnership with France in January 1998.
- In the past 25 years, through numerous bilateral meetings, a strong institutional mechanism has been established to strengthen cooperation between India and France in space, defense, civil nuclear, renewables, cyberspace, digital technology, counter-terrorism, and the blue economy sectors.
- India and France at the Paris Climate Change Summit in 2015 jointly launched International Solar Alliance to promote solar energy in 121 tropical countries all over the world. India and France enjoy synergy in the defense sector.
Introduction
- India and France have traditionally close and friendly relations. In 1998, the two countries entered into a Strategic Partnership which is emblematic of their convergence of views on a range of international issues apart from a close and growing bilateral relationship.
Areas of Cooperation
- The areas of defense cooperation, space cooperation and civil nuclear cooperation constitute the three principal pillars of our Strategic Partnership.
- Apart from these traditional fields of cooperation, India and France are increasingly engaged in new areas of cooperation like climate change, sustainable growth and development, the International Solar Alliance, etc.
About India and France’s strategic partnership
- India and France support a multi-polar world order. France has continued to support India’s claim for permanent membership of the Security Council and the reforms of the United Nations.
- France has provided consistent support to India’s candidature for the membership of all four Multilateral Export Control regimes, viz. Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), the Wassenaar Arrangement (WA) and the Australia Group (AG).
- France’s support was vital in India’s accession to MTCR, WA and AG while France continues to support India’s bid for accession to the NSG.
Background
- India and France have traditionally close and friendly relations. In 1998, the two countries entered into a Strategic Partnership which is emblematic of their convergence of views on a range of international issues apart from a close and growing bilateral relationship.
- The areas of defense & security cooperation, space cooperation and civil nuclear cooperation constitute the principal pillars of the Strategic Partnership.
- India and France also have a robust economic partnership. Apart from these, India and France are increasingly engaged in new areas of cooperation such as maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region, counter-terrorism, climate change, renewable energy and sustainable growth and development among others.
Present status of relations:
- After our 1998 nuclear tests, when France declined to impose bilateral sanctions on us and demonstrated a far deeper understanding of India's security imperatives than other nations, we launched a Strategic Dialogue with them.
- Bilateral trade with France has been steadily increasing over the previous decade and is expected to reach USD 10.75 billion in 2020. The two sides also agreed that moving on with talks on an India-EU trade and investment pact was critical.
- In 2005, a deal was made for the construction of six Scorpène submarines in India with French assistance.
- In 2003 and 2011, joint exercises between the air forces (Garuda series) and armies (Shakti) were established.
- The 36 Rafale aircraft were purchased under a government-to-government transaction.
- Negotiations between the Nuclear Power Corporation of India (NPCIL) and Areva for the construction of six EPR (European Pressurized Reactors) nuclear power reactors with a total capacity of 9.6 GW began around a decade ago.
Defence Cooperation
Purchase of Rafale aircraft:
- The Inter-governmental agreement for the purchase of 36 Rafale jets by India in flyaway condition was signed in New Delhi on 23 September 2016 by Raksha Mantri Manohar Parrikar and French Defence Minister Le Drian. Project implementation is underway.
P-75 Scorpene Project:
- The contract for six Scorpene submarines from M/s DCNS was signed in October 2006. All six vessels are to be built under technology transfer at the Mazagaon Docks Ltd. Project implementation is underway. The first submarine INS Kalvari was commissioned in October 2017.
Space Cooperation
- India and France have a rich history of cooperation in the field of space, since the 1960s with the construction of the Sriharikota launch pad with French technical assistance. Building on the historical linkages in the arena of civilian space, both India and France issued a “Joint Vision for Space Cooperation” during the visit of President Macron to India in March 2018.
- ISRO and the French Space Agency, CNES have been carrying on various joint research programmes and collaborating in satellite launches.
- Both sides have exchanged cooperative proposals addressing Earth observation, Maritime domain awareness, Global navigation satellite system, exploration of the solar system, space transportation system and human spaceflight.
- As part of the ongoing bilateral cooperation between ISRO and Arianespace, recently GSAT-24 communication satellite of New Space India Ltd (NSIL) was successfully launched on board Ariane-5 from Kourou, French Guiana.
Civil Nuclear Cooperation
- An agreement on civil nuclear cooperation was signed between India and France on 30 September 2008 during the visit of then Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh to France.
- Subsequently, during the visit of then-French President Nicolas Sarkozy to India in December 2010, the General Framework Agreement and the Early Works Agreement between NPCIL and M/s AREVA for the implementation of EPR for the Jaitapur Nuclear Power Project (JNPP) were signed.
- Both countries are working to conclude technical and financial matters for an early conclusion of this important project.
- Further, India is a member of ITER, a multi-national consortium formed to construct an experimental fusion reactor, located in Cadarache, India's role in the ITER project is managed by the Department of Atomic Energy.
Concerns between India-France relations:
- Despite their friendly connections, the bilateral cooperation between the two countries faces some challenges. France and India do not yet have a Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Furthermore, there has been no development on the India-EU Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA). This led to a lack of free flow of trade and commerce between the nations.
- Despite a robust defense alliance, the two nations have differing defense and security cooperation agendas and approaches.
- The concentration of India on its neighborhood and its "non-aligned" strategy can often collide with France's global goals.
- Despite being strong trading partners, India and France have a trade imbalance, with France exporting more to India than the other way around. This imbalance has been a cause of worry for India, and both nations are seeking solutions.
- France has accused India of failing to appropriately protect intellectual property rights, harming French enterprises working in India. And most importantly, as discussed above, both India and France are concerned about China's growing influence in the Indian Ocean region, which has the potential to disturb the regional balance of power and endanger regional peace and security.
Way Ahead
- A strengthened India-France alliance will offer enormous value to a region blighted by a binary polarisation of power caused by escalating US-China competition, which comes at the price of regional countries seeking to safeguard their interests, security, and prosperity.
- Given their significant material capacity and shared interests and concerns in the region, both states will need to consistently evolve and operationalize the potentials of their strategic relationship to address the ongoing shifts in the Indo-security Pacific's and geopolitical architecture.
- France might be an important IOR partner for India. The access to French military stations in the Indian Ocean region allows India more leeway. France, with an active presence in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, might be a dependable partner for India in the broader Indo-Pacific context.
- Long-range and maritime capabilities, surveillance, aircraft carriers, nuclear submarines, drones, and cyber warfare have been deployed across the Indo-Pacific in pursuit of force projection, making this area unpredictable, hazardous, and prone to great power confrontation.
- In such a setting, strategic partnerships between India and France in the IOR can assist in ensuring peace, stability, and security in the larger IPR by cooperating and incorporating other regional players.
Closing Remarks
- French social security legislation, long-term student visas, and the ability to work for two to three years to pay off student loans are just a few of the issues that need to be resolved for the two nations to collaborate more effectively.
https://newsonair.gov.in/Main-News-Details.aspx?id=464092
Color-coded Warnings by the IMD
Context
- IMD issued a red alert for Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim, and Meghalaya as these states are expected to experience heavy to very heavy rainfall.
Details
- The India Meteorological Department has issued a red alert for Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim and Meghalaya as these states are expected to experience heavy to very heavy rainfall with extremely heavy rainfall today.
- Red alert has been issued in West Bengal and Sikkim for tomorrow as well.
- The IMD has asked people to avoid areas prone to waterlogging and stay away from vulnerable structures. Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are under an orange alert as heavy to very heavy rainfall is expected in the two states.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
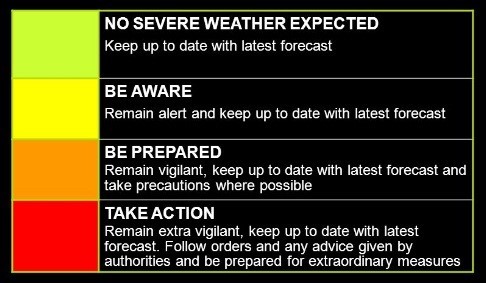
About the Colour Code of IMD:
|
Green (All is well)
|
|
|
Yellow (Be Aware)
|
- Yellow indicates severely bad weather spanning several days. It also suggests that the weather could change for the worse, disrupting day-to-day activities.
|
|
Orange/Amber (Be Prepared)
|
- The orange alert is issued as a warning of extremely bad weather with the potential of disruption in commute with road and rail closures, and interruption of power supply.
|
|
Red (Take action)
|
- When extremely bad weather conditions are certainly going to disrupt travel and power and have significant risks to life, the red alert is issued.
|
About IMD
- Under Ministry: The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- Aim: It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.
- Headquarters: IMD is headquartered in Delhi and operates hundreds of observation stations across India and Antarctica.
- Regional Offices: Regional offices are in Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Nagpur, Guwahati and New Delhi.
- Working: IMD operates a network of hundreds of surface and glacial observatories, Upper Air (high altitude) stations, ozone and radiation observatories and meteorological radar stations.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=IMD-issued-red-alert-for-Bihar%2c-West-Bengal%2c-Sikkim%2c-and-Meghalaya-as-these-states-expected-to-experience-heavy-to-very-heavy-rainfall&id=464101
Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres
Context
- The government has said that over one lakh 60 thousand Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres have been operationalized across the country.
Details:
- These centers deliver a range of comprehensive health care services like maternal and child health, and services to address communicable and non-communicable diseases.
- It also provides free essential medicines and diagnostic services, teleconsultation, and health promotion including wellness activities like Yoga.
- In a tweet, Union Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya said, Health and Wellness Centres are contributing immensely towards creating a healthy and prosperous India.
About Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs)
- Ayushman Bharat (AB) is an attempt to move from a selective approach to health care to deliver a comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care. It has two components that are complementary to each other.
- Under its first component, 1,50,000 Health & Wellness Centres (HWCs) will be created to deliver Comprehensive Primary Health Care, that is universal and free to users, with a focus on wellness and the delivery of an expanded range of services closer to the community.
- The second component is the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) which provides health insurance coverage of 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families seeking secondary and tertiary care.
- Launched: It was launched in 2018 as a part of the broader Ayushman Bharat initiative.
- Features:
- They deliver a comprehensive package of services that address the health needs of the population, ranging from maternal and child health, communicable and non-communicable diseases, oral health, eye care, mental health, geriatric care, emergency care, and basic diagnostics.
- They are manned by a team of competent and dedicated health workers, headed by a mid-level health provider (MLHP), who is either a nurse or an Ayurveda practitioner with additional training in public health.
- Significance:
- They enhance the accessibility and availability of primary health care services, especially for the rural and urban poor. They are located close to the communities and offer a range of services, such as screening, diagnosis, treatment, referral, counseling, and follow-up.
- They reduce the burden of disease and disability by focusing on prevention and early detection of common conditions. They cover priority areas, such as maternal and child health, non-communicable diseases, mental health, oral health, eye care, and geriatric care.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Over-one-lakh-60-thousand-Ayushman-Bharat-Health-and-Wellness-Centres-operationalised-across-country%2c-said-govt&id=464090
Ukraine urges to join NATO membership
Context
- NATO member countries yesterday said that Ukraine can join the military alliance when allies agree and conditions are met.
Details
- President Volodymyr Zelensky criticized the lack of a timeframe and vague language regarding the conditions for inviting Ukraine. He also accused the alliance of providing Russia with motivation for invasion.
- In a statement, NATO's Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg emphasized that the alliance had made significant decisions and conveyed a strong message of support for Ukraine.
- He acknowledged Zelensky's concerns but stressed the importance of Ukraine prevailing in its war with Russia before discussing membership.
- The G7 group of nations is expected to issue a declaration on how they will help Kyiv defeat Russia and deter any new aggression in the coming years. The announcement will provide a framework under which individual nations will later agree on bilateral deals with Kyiv detailing the weapons they will give.
About NATO
|
About
|
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 31 member states – 29 European and two North American.
|
|
Purpose
|
- It aims to protect the security and freedom of all the countries that are members (the Allies).
|
|
Established
|
- Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4th April 1949.
|
|
Headquarters
|
- NATO's main headquarters are located in Brussels, Belgium, while NATO's military headquarters are near Mons, Belgium.
|
|
Functions
|
- NATO is an active and leading contributor to peace and security on the international stage.
- It promotes democratic values and is committed to the peaceful resolution of disputes.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Ukraine-can-join-military-alliance-when-allies-agree-and-conditions-met%2c-said-NATO-member-countries&id=464099
World Population Day
Context
- The day is observed on the 11th of July every year. The objective of the day is to increase the awareness of the people towards the worldwide population issues.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
About:
- World Population Day, which seeks to focus attention on the urgency and importance of population issues, was established by the then-Governing Council of the United Nations Development Programme in 1989.
- By a resolution in December 1990, the United Nations General Assembly decided to continue observing World Population Day to enhance awareness of population issues, including their relations to the environment and development.
- First observed: The Day was first marked on 11th July 1990 in more than 90 countries.
- Theme 2023: The theme for World Population Day 2023 is 'Unleashing the power of gender equality: Uplifting the voices of women and girls to unlock our world's infinite possibilities.'
Population Trends
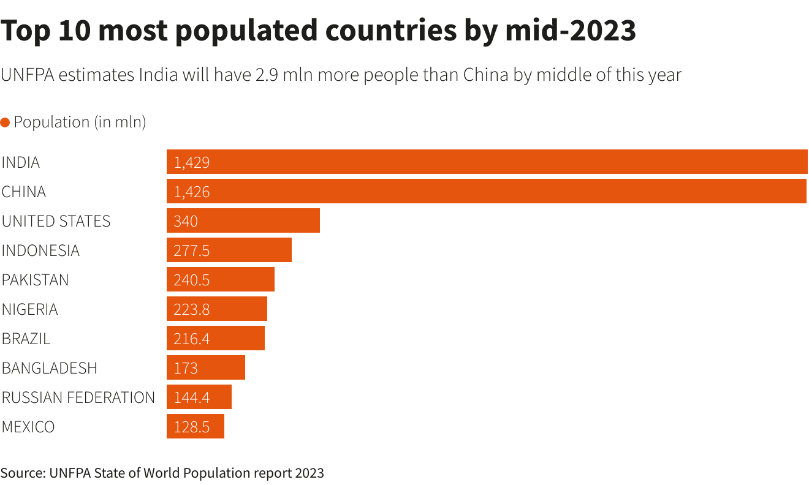
- India to overtake China: India is set to overtake China to become the world’s most populous country by the middle of 2023.
- India’s estimated population: India's population by mid-year is estimated at 1.4286 billion, against 1.4257 billion for China- 2.9 million fewer.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Today-is-World-Population-Day&id=464017







