WOMEN-LED DEVELOPMENT
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi said India has moved from women development to women-led development in the last nine years.
Overview
- India’s vision is well encapsulated in our Hon’ble Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s remark at the G20 Summit in Bali, “global development is not possible without women’s participation.”
- There is substantial evidence to support that with increased internet and mobile penetration, female entrepreneurship has scaled substantially in India. With an estimated 5 million to 15.7 millionMSMEs and agribusinesses, India has more women-owned enterprises compared to many other countries.
Key Finding
- According to a McKinsey report, India can add up to 18% to its GDP (approximately $ 770 billion), provided it bridges its gender equality gap by improving female workforce participation in the country.
- In addition to job creation by private and government sectors, entrepreneurship is a powerful yet largely untapped opportunity for working-aged women in India.
- By creating jobs, fuelling innovation and advancing investments in health and education, entrepreneurship among women can help transform India’s journey towards social and economic growth.
Approaches To Women Inclusive Development In India:
- From first to fifth five year plan welfarism based approach was followed. It involved protective patronage.
- From 6th five year plan gender inclusive development was emphasized. For first time, entire chapter focused on women was incorporated (Women and Development).
- 9th five year plan adopted women empowerment as national development policy goal.
- 11th five year plan is considered as the watershed Plan as far as women inclusive development is concerned.
- It introduced two major concepts:
- Women governance: gender justice, gender equality, gender budgeting, gender sensitivity.
- Life cycle approach: physical security, social security, economic security, political empowerment, community security.
EXAMPLES HIGHLIGHTING THE DEVELOPMENTS IN THE AREA OF WOMEN EMPOWERMENT ARE:
- The first female fighter pilots have been appointed in the Indian Air Force.
- India’s successful launch of the Mangalyaan and 104 Nano satellites on-board a single rocket had a team of women scientist behind them.
- India has been successful in achieving gender parity in school education. The literacy rate of women has risen from a mere 9 per cent in 1951 to 65 per cent in 2011.
- Today, every fourth worker in India is a woman.
- One third of all certified engineers are now women and over three fourths of all health workers at primary level are women.
- In a country bursting with entrepreneurial spirit, today almost every fifth entrepreneur is a woman.
- Elected women representatives now make up about 46 percent of panchayat members.
- In the 1957 elections only 45 women had contested general elections, in the 2014 election, 668 women candidates contested.
- The average life expectancy of women has risen from 31.7 years in 1950-51 to about 70 years in 2016.
- Institutional births have risen to an all- time high of 79 per cent in 2014-15.
- The maternal mortality rate has dropped by half in the decade between 2001-03 and 2011-13.
Issues persisting
- In the WEF's report released in July 2022, India was ranked low at 135th place in terms of gender parity.
Population
- In 2011, the sex ratio was 943 and the same for rural and urban areas was 949 and 929.
- Sex ratio in the age group 0 - 6 years declined in urban area.
- As per National Sample Survey (2011), only 11.5% households in rural areas and 12.4 % households in
- urban areas are female headed households.
Health
- Health and Survival index: India has fared the worst, ranking at 155.
- China and India together account for about 90 to 95% of the missing female births annually.
Literacy And Education
- As per NSS 75th Round, only 8.3% of the females of age 15 years & above by highest level of education
- have successfully completed graduation and above level of courses.
- As per NSS 75th Round, only 3.1 % females are pursuing technical/professional courses.
- In the index of education attainment, India has been ranked at 114.
Participation In Economy
- As per Global Gender Gap Report 2021, economic participation gender gap actually widened in India by 3% this year.
- The earned income of women in India is only one-fifth of men’s.
- Only 8.9% of firms have women in top management positions
Participation In Decision Making
- India has declined on the political empowerment index by 13.5 percentage points, and a decline in the number of women ministers, from 23.1% in 2019 to 9.1% in 2021.
- In the 17th Lok Sabha, only 14% of the total members are women.
- Women participation in the State Assemblies was 11% against the total elected representatives.
- Only 9% of judges in Supreme Court are females.
- Percentage of Female Police Officers in India is a meagre 7.02.
- 108th Constitutional Amendment has still not seen light of the day.
Social Obstacles in Women’s Empowerment
- Crimes against women increased 7.3 per cent from 2018 to 2019.
STEPS TAKEN BY THE GOVERNMENT TO END THE EXISTING DISCRIMINATION:
Financial Empowerment
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Programme and Sukanya Samridhi Yojana
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana
Encouraging Entrepreneurship
- Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana,
- Self Help Groups (SHGs) have been promoted under the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM).
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojna
- Support to Training and Employment Programme for Women (STEP) scheme
- E-haats
Empowering Motherhood, Health
- The Maternity Benefit Act has been amended to extend the period of mandatory paid maternity leave
- for working women to 26 weeks.
- PM Matru Vandana Yojana.
- PM Ayushman Bharat and Health & Wellness Centres
- Swatch Bharat Mission
- POSHAN Abhiyaan
Women Safety
- Strict implementation of the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013.
- Women Helplines and One Stop Centres
- 33 per cent reservation for women in the police force is also being implemented.
- Nirbhaya Fund
- Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020
- Ujjawala Scheme
Accessing the Inaccessible
- Mahila Shakti Kendra scheme.
Moving Forward
- Under its G20 presidency, India has identified eight priority areas, including inter alia women-led development and public digital infrastructure.
- G20 EMPOWER platform’s three priority areas are to convert these dialogues to action through the following approaches.
- Promoting women’s entrepreneurship is among India’s most important growth and equality priorities. It is a powerful vehicle that can speed up India’s journey of becoming a $5-trillion economy. Moreover, it is one of the most significant factors that will help raise household incomes, alleviate poverty, and help us achieve the 2030 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG-5 on gender equality.
- India’s promotion of Nari Shakti is reflected in various government initiatives. The National Rural Livelihood Mission supports rural women’s entrepreneurship, with over 80 million women participating in 7.5 million self-help groups. The Mudra scheme enables access to finance and the GeM portal reserves 3% of all government procurement for women entrepreneurs.
- Research by Niti Aayog indicates that women’s entrepreneurship needs support to make them sustainable and autonomous and bring them into the formal sector. The employment-generating capacities of these enterprises are well-documented and create collateral gains for society and economy.
- Under its G20 presidency, India has identified eight priority areas, including inter alia women-led development and public digital infrastructure. In addition, the G20 Alliance for the Empowerment and Progression of Women’s Economic Representation (G20 EMPOWER), led by the ministry of women and child development, aims to shift the narrative from women’s development to women-led development. Women entrepreneurs are at the heart of this shift, leading G20 EMPOWER.
- We must transform challenges into opportunities and accelerate the shift towards greater inclusion of women in the workforce and women-led entrepreneurship. As SDGs demonstrate, adopting a gender lens and creating a culture to provide more opportunities to women requires collaborative and concerted action within our country and globally.
- Digitalisation is a powerful tool that can help strengthen women’s economic participation. In addition, there are several sectors where remote working can be a permanent feature and offer the opportunity to employ women workforce.
- G20 EMPOWER platform’s three priority areas are to convert these dialogues to action through the following approaches.
- One, focus on women’s entrepreneurship: Increase women’s access to skilling, capacity building, support infrastructure, and finances to promote women-led and women-owned businesses. Two, create a partnership for promoting women’s leadership aimed at increasing their public representation, access to public amenities, and enhancing participation in the labour force in public and private sectors. Three, work towards education that facilitates women’s representation in decision-making roles.
- The Women Entrepreneurship Platform (WEP) is a key conduit to bridge the knowledge gap: As Indian women and girls make rapid strides and transition from the education system into the world of work, India is creating a strong entrepreneurship pathway for an additional 55 million women who could enter the workforce by 2030.
- Announced at the Global Entrepreneurship Summit 2017, the ideation and incubation of WEP happened at Niti Aayog. Today, it is a shining example of a robust public-private partnership, providing multisectoral support to women entrepreneurs. It is building the pipeline of women entrepreneurs through awareness, training, skilling, access to finance and marketing needs. WEP has also emerged as a thought leader by producing data that help better understand women’s entrepreneurship needs with a sharp focus on leadership and mental health. Also planned is an emphasis on technology, lowering barriers to allow women to avail multiple efficiencies without mandating a traditional brick-and-mortar approach to optimising growth.
.jpeg)
'BEGGAR-FREE CITY'
Context
- In Maharashtra, a new initiative called 'beggar-free city' has been started in Nagpur. Commissioner of Police of Nagpur City, Amitesh Kumar said that, notification of 144 CrPC has been issued in this regard.
Details
- Notices have been served to people. While speaking to reporters he said that they will strictly enforce this and begging will not be allowed in public places.
- This is the joint venture of Nagpur City police and Nagpur Municipal Corporation’s (NMC) social welfare department.
- The NMC has made special arrangements to accommodate homeless people in the shelters owned by it.
- The civic body has kept a bus and an ambulance ready to shift the beggars caught in police drive to its shelter home.

'PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman'
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi will address the post-budget webinar on 'PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman'.
Details
- The webinar is part of a series of 12 post-budget webinars being organised by the government to seek ideas and suggestions for effective implementation of the initiatives announced in the Union Budget 2023.
- PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman aims at improving the quality, scale and reach of products and services of artisans, by integrating them with the domestic and global value chains.
- The webinar will have four breakout sessions on themes, including access to affordable finance and social security, advanced skill training and access to modern tools and technology. The webinar will also deliberate upon themes, including marketing support for linkages with domestic and global markets, identification of beneficiaries and implementation framework.

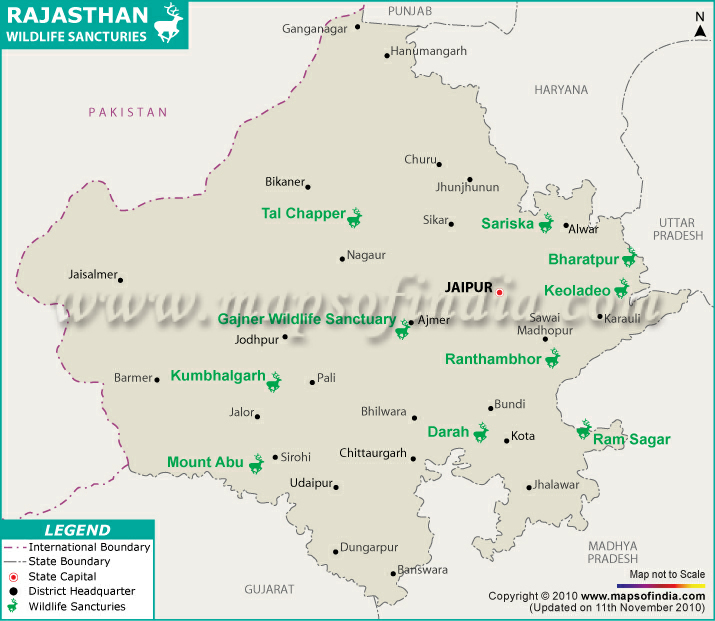
SARISKA TIGER RESERVE AND RANTHAMBORE NATIONAL PARK
Context
- A tigress named, T 134 has been shifted from Ranthambhore National park to Sariska Tiger Project in Alwar, Rajasthan.
About Sariska Tiger Reserve:
- Located in: This tiger reserve is located in
- It became part of India'sProject Tiger in 1978.
- Tiger relocation:It is the first reserve in the world with successfully relocated tigers.
- It is an important biodiversity areain the Northern Aravalli leopard and wildlife corridor.
- It is rich in mineral resources, such as
- It is a part of the Aravalli Range and the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests eco-region.
Ranthambore National Park Rajasthan
- Ranthambore National Park is amongst the few green areas of India’s desert state of Rajasthan. The forest is mainly grassland, and dry deciduous trees outnumber evergreen plants.
- This famous jungle in Indiais named after the famous Ranthambore Fort. In 1955, It was first started as Sawai Madhopur Game Sanctuary. Later, it joined Sawai Man Singh Sanctuary and Keladevi Sanctuary to form a tiger reserve of 1,334 sq km.
- This national park has over 300 different types of plant species. The Ranthambore National Park Rajasthan trees are Dhok, Banyan, Pipal, Mango, Jamun, Neem, Ber, Babul, Gum, Gurjan, Khajur, Kadam, Khair etc.
- Ranthambore National Park is in Sawai Madhopur district of Rajasthan state. It covers an area of 1,334sq km.
- Ranthambore is a tiger reserve. Leopards, Striped Hyenas, Sambar deer, Chital, Nilgai, Langurs, Macaques, Jackals, Jungle cats, Caracals, Sloth bears, Blackbucks, Rufous-tailed Hare, Indian Wild Boar, Chinkara, etc., have inhabited this dry forest.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Rajasthan%3a-Sariska-gets-another-tiger%2c-count-hits-28&id=457156
YAOSHANG FESTIVAL
Context
- The Yaoshang festival has begun in Manipur.
Details
- The festival is celebrated by the Meetei who are predominantly Hindu and it is celebrated at the same time as Holi.
- However, during the Yaoshang festival, apart from playing with colour, the festival also witnessed a number of cultural and religious activities for five days.
- From some years back, the village level sport competition held by different clubs or organisations during the Yaoshang festival has become a major feature of the celebration.





