AIR INDIA RADIO
The organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) has criticised India over the delimitation exercise in Jammu Kashmir.
In News
- The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) has criticised India over the delimitation exercise in Jammu Kashmir.
- The Indian spokesperson slammed the OIC for its “unwarranted” comments and also asked to refrain from carrying out its “communal agenda” at the behest of one country, in an oblique reference to Pakistan.
- Non-interference in internal matters of other countries is one of the principles of India’s foreign policies. India always believed in peaceful co-existence with all countries, including its neighbours.
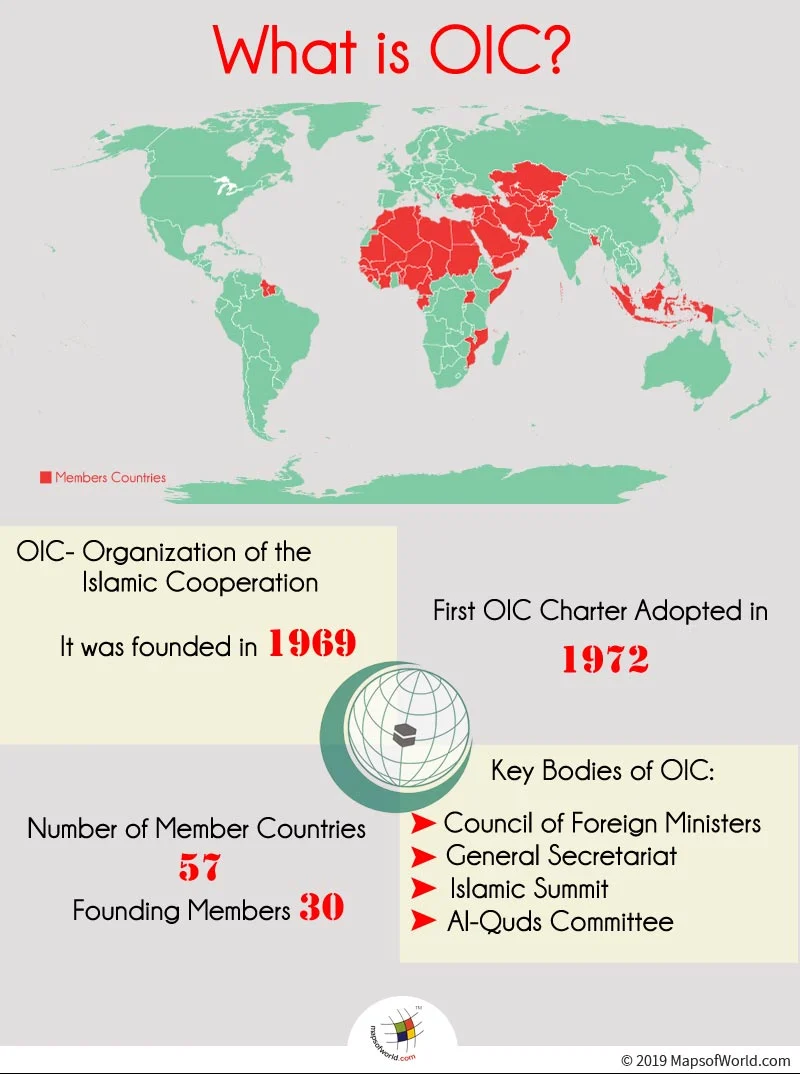
About OIC
- The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is the second-largest organization after the United Nations with a membership of 57 states spread over 4 continents.
- The Organization is the collective voice of the Muslim world.
- It endeavours to safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony among various people of the world.
Background
- The Draft published by the Delimitation Commission for the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly has started a controversy.
- Out of the 90 Assembly Constituencies in the region, 43 will be part of the Jammu region and 47 of the Kashmir region.
- Under the draft published, some villages in one constituency are surrounded by villages of another.
- The Delimitation Commission of Jammu and Kashmir is chaired by retired Justice Ranjana Prakash Desai and includes Chief Election Commissioner Sushil Chandra and the State Election Commissioner as ex-officio members.
- As per Article 170, the states get classified into territorial constituencies after every census, according to the Delimitation Act.
About Delimitation Commission of India
- Delimitation means the act or process of fixing limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies in a country or a province having a legislative body.
- Article 82 - Parliament by law enacts a Delimitation Act after every Census.
- The Delimitation Commission is appointed by the President of India and works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
- The main task of the commission is redrawing the boundaries of the various assembly and Lok Sabha constituencies based on a current census.
- The representation of each State is not changed during this exercise. However, the number of SC and ST seats in a state is changed in accordance with the census.
- The present delimitation of constituencies has been done based on the 2001 census under the provisions of the Delimitation Act, 2002.
- The Commission is a powerful and independent body whose orders cannot be challenged in any court of law.
- The orders are laid before the Lok Sabha and the respective State Legislative Assemblies. However, modifications are not permitted.
- Delimitation commissions have been set up four times in the past; 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002, under the Delimitation Commission Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002.
- The present delimitation of parliamentary constituencies within states has been done based on the 2001 census.
- According to the 84th amendment, the present constituencies carved out based on the 2001 census shall continue to be in operation till 2026.
Functions of Delimitation Commission
- The Delimitation Commission has to determine the number and boundaries of constituencies in such a manner that the population of all seats is the same, as far as practically possible.
- The Commission also identifies the seats to be reserved for the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes communities, in areas where their population is significant.
- The Commission releases draft proposals to the public through the Gazette of India and the official gazettes of states, and also in regional language newspapers.
- It also conducts public sittings wherein the public’s opinion is heard through written or oral representations.
- If found appropriate, changes are made to the draft proposal.
- The final order is published in the Gazettes and comes into effect by a date specified by the President.
Delimitation challenges
- The present delimitation is based on the census of 2001, whereas the total number of seats in the Parliament and the Legislative Assemblies is fixed as per the census of 1971.
- The Constitution of India has put a cap on the maximum number of seats in the Lok Sabha to 550 and Rajya Sabha to 250. Therefore an increasing number of populations are being represented by a single representative.
NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
UDAN Scheme
- The Union Government plans to encourage smaller aircraft, seaplanes and helicopters under the UDAN scheme.
- Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik or UDAN is a regional airport development programme of the Union Government and also a part of the Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS).
- The main objective is to upgrade under-serviced air routes and to promote air transport infrastructure development in all regions and states of India.
- Its goal is to make air travel affordable, boost economic development, and promote job growth.
- The UDAN Scheme is a key element of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) which was released by the Ministry of Civil Aviation (India) in 2016.
- It is jointly funded by the Union government and state governments.
- Develop new airports and enhance the existing regional airports to increase the number of operational airports with regularly scheduled flights.
- The UDAN scheme will run for 10 years and can be extended thereafter.
- Concessions from the Union Government;
- Created a Viability Gap Funding (VGF) to subsidise the airfare.
- Concession on service tax on tickets.
- Concessions from State Governments;
- Reduction of GST for 10 years.
- Coordinate with oil companies to create fuelling infrastructure on airports.
- Provide free land for the development of the airport, with multimodal (rail, road, metro, waterways, etc.) hinterland connectivity.
- Provide free security Systems and manpower.
- Provision of water, electricity and other utilities at a reduced rate.
- 20% share of Viability Gap Funding; North-Eastern states, Uttrakhand, Himachal Pradesh and Union territories to provide 10% share only.
- Concessions from airport operators;
- No landing, parking or other charges.
- No Terminal Navigation Landing Charges.
- There is a cap of maximum fare of Rs 2,500 per hour of flight for 50% of the seats, connecting un-served and underserved regional airports, the remaining 50% of seats will be priced at market rate.
- For helicopter services, the maximum fare is also capped at Rs 2,500 for every 30-minute leg of the flight.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=UDAN-is-a-huge-leap-forward-in-direction-of-democratization-of-air-travel-envisioned-by-PM%3a-Civil-Aviation-Minister&id=441151
Malviya Mission
- “Malviya Mission” launched for capacity building of teachers/faculty in higher education institutes.
- The Union Minister of Education Shri Dharmendra Pradhan launched the “Malviya Mission” to develop an environment for teacher education/faculty development across the country.
- He highlighted the need to adopt a multidisciplinary approach in teacher education with a special focus on Indian values, languages, knowledge, ethos, and traditions.
- He stressed focusing on teacher education to achieve the targets mentioned in the ‘National Education Policy 2020’.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Education-Minister-reviews-report-on-institutional-mechanism-for-capacity-building-of-teachers%2c-faculty-in-higher-education-institutes&id=441142
Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary
- The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) Bhupender Yadav has notified Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary as 52nd Reserve Forest for Wild cats.
- The newly notified tiger reserve includes the tiger habitat between Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in the northeast and Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on the southern side and facilitates the dispersal of tigers from Ranthambore Tiger Reserve.
- The Ramgarh Vishdhari Sanctuary will be spread across 1,071 sq km.
- A 302 sq Km area in the notified tiger sanctuary will be left as critical habitat for Tigers and the rest of the area will act as a buffer zone for the Ranthambore National Park.
- Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary was established in 1982.
- The core areas of the sanctuary have 8 villages and are home to large numbers of wild animals like sambhars, caracals, wild boars, nilgai, and striped hyenas.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Ramgarh-Vishdhari-Wildlife-Sanctuary-notified-as-52nd-Reserve-Forest-for-Wild-cats&id=441092
PM visit to Lumbini, Nepal
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Lord Buddha’s birthplace Lumbini district of Nepal for Buddha Purnima.
- The focus on Lumbini has been part of the “Buddhist Circuit” vision of the Indian government, which has presented India as the land of the Buddha.
- India has been focusing on the Buddhist community worldwide as part of its soft power diplomacy.
- India-Nepal Relation
- Nepal is an important neighbour of India and occupies a special significance in its foreign policy because of the geographic, historical, cultural and economic linkages/ties that span centuries.
- India and Nepal share similar ties in terms of Hinduism and Buddhism with Buddha’s birthplace Lumbini located in present-day Nepal.
- The India-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950 forms the bedrock of the special relations that exist between India and Nepal.
- India is Nepal’s largest trade partner and the largest source of foreign investments, besides providing transit for almost the entire third-country trade of Nepal.
- India-Nepal has undertaken various connectivity programs to enhance people-to-people linkages and promote economic growth and development.
- Bilateral defence cooperation includes assistance to the Nepalese Army in its modernization through the provision of equipment and training.
- India has signed three sister-city agreements for twinning Kathmandu-Varanasi, Lumbini-Bodhgaya and Janakpur-Ayodhya.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-reaches-Kushinagar-after-concluding-his-visit-to-Nepal%2c-offers-prayers-in-Mahaparinirvana-Mandir&id=441091
International Migration Review Forum
- Minister of State for External Affairs, represented the Indian delegation for the First International Migration Review Forum to be held by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in New York.
- The forum serves as the primary inter-governmental global platform to discuss and share the progress on implementation of all aspects of migration and its intersection with the Sustainable Development Goals.
- International Migration Review Forum (IMRF)
- The IMRF was created by the Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration (GCM), the member states with the participation of stakeholders to discuss the implementation of the GCM.
- The forum will be in the framework of the United Nations through a State-led approach and with the participation of all relevant stakeholders.
- The UNGA members further decided that the high-level dialogue currently scheduled to take place in the every-fourth session of the General Assembly.
- The Forum will be an opportunity to understand what has changed since 2018, particularly the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on migrant workers’ rights, and to address new and emerging issues, such as the impact of climate change on migration.
- The meeting hopes to galvanise political will and momentum towards the implementation of the Compact and its objectives for the benefit of migrant workers, countries of origin, and countries of destination alike.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=MoS-External-Affairs-V.-Muraleedharan-to-lead-Indian-delegation-for-First-International-Migration-Review-Forum&id=441102




