INDIA'S RISING DEFENCE CAPABILITIES
Context
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi has said that India is fast emerging as a big global player in the defence sector and the capabilities of its security forces are constantly rising.
Key Details:
- Addressing soldiers at Lepcha in Himachal Pradesh, Mr Modi said the circumstances of the world are such that the expectations from India are constantly rising.
- At such an important time, it is necessary that India's borders are protected and there is an environment of peace in the country and our soldiers have a big role in this.
- Prime Minister said, India is protected till the time our brave hearts are standing on the borders like the Himalayas. Mr Modi said, that after Independence, these brave hearts fought so many wars and won the country's hearts.
- He said, our jawans have snatched victory in the face of challenges. Prime Minister said India's soldiers have always walked ahead, risking their lives, and have always proven that they are the 'strongest wall' at the borders, Mr Modi said, For me, a place where our security forces are deployed is no less than a temple.
- The prime minister also hailed the role played by the armed forces in evacuations in earthquake-hit areas and during other calamities. Mr Modi celebrated this year's Diwali at Lepcha in Himachal Pradesh yesterday.
Defending the World
| The Indian Defence sector, the second largest armed force is at the cusp of revolution. The Government has identified the Defence and Aerospace sector as a focus area for the ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ or Self-Reliant India initiative, with a formidable push to establish an indigenous manufacturing infrastructure supported by a requisite research and development ecosystem. |
- In the Union Budget 2023-24, the Capital Allocations for modernization and infrastructure development of the Defence Services have been increased to INR 1,62,600 Cr representing a rise of 6.7% over FY 2022-23. The industry gets INR 5.94 Lakh crore in Budget 2023-24, a jump of 13% over the previous year.
- The Ministry of Defence has set a target of achieving a turnover of INR 1.75 lakh crore in aerospace and defense Manufacturing by 2025, which includes exports of INR 35,000 crore.
- Till April 2023, a total of 606 Industrial Licences have been issued to 369 companies operating in Defence Sector.
Industry Scenario:
Defence Production and Export Promotion Policy 2020 (DPEPP):
- The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has formulated a draft DPEPP 2020 as a guiding document of MoD to provide a focused, structured, and significant thrust to the defence production capabilities of the country for self-reliance and exports.
Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP 2020):
- DAP 2020 aims to empower the Indian domestic industry through the Make in India initiative and it has Laid down a strict order of preference for procurements and has adequately included provisions to encourage FDI to establish manufacturing hubs both for import substitution and exports while protecting the interests of Indian domestic industry.
- Salient features of DAP 2020:
- Reservation in Categories for Indian Vendors.
- Enhancement of Indigenous Content.
- Rationalisation of Trial and Testing Procedures.
- Make & Innovation.
- Design & Development.
- Industry Friendly Commercial Terms.
- Offsets.
Growing Demand:
- Demand growth is likely to accelerate with rising concerns about national security.
- Till October 2022, a total of 595 Industrial Licences have been issued to 366 companies operating in Defence Sector.
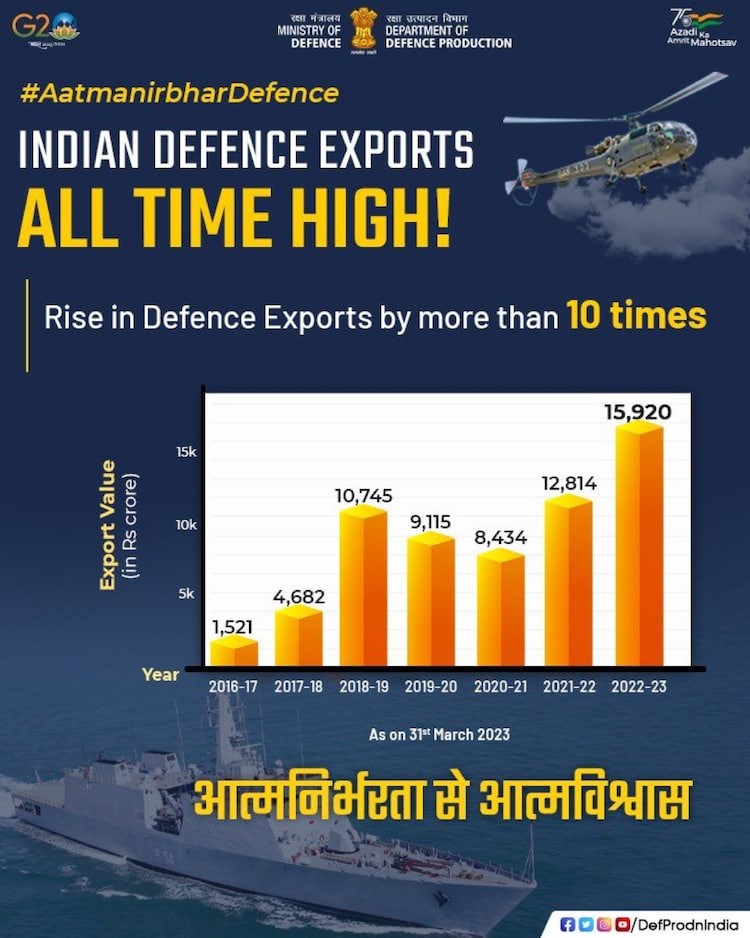
- Defence exports grew by 334% in the last five years; India now exports to over 75 countries due to collaborative efforts.
- The Ministry of Defence has set a target of achieving defence exports worth Rs. 35,000 crore (US$ 4.27 billion) by 2024.
Competitive Advantage
- India has the world's third-largest defence expenditure, as of 2021, and expects to export equipment worth US$ 15 billion by 2026.
- The Government of India opened the defence industry for private sector participation to provide impetus to indigenous manufacturing.
- As per the Union Budget 2022-23, 25% of the defence R&D budget has been earmarked for private industry and start-ups which will pave the way for the innovation of new defence technologies in India.
MARKET SIZE
- According to the global power index, the Indian defence sector ranks fourth in terms of firepower with a score of 0.0979 (with 0.0 being the perfect score).
| The Indian government has set the defence production target at US$ 25 billion by 2025 (including US$ 5 billion from exports by 2025). India is one of the world’s biggest defence spenders with a total outlay of Rs. 5.25 lakh crore (US$ 66 billion), accounting for 13.31% of the total budget and indicating an increase over the budget estimates of 2021-22 by Rs. 46,970 crores (US$ 5.9 billion). |
- India’s military spending of US$ 76.6 billion ranked third highest in the world in 2021. This was up by 0.9% from 2020 and by 33% from 2012.
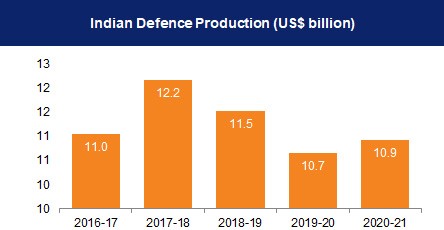
- The value of defence production in the country crossed Rs. 1 lakh crore (US$ 12 billion) for the first time on the back of key reforms to spur growth in the sector that holds vast potential.
- The figure stood at Rs. 1,08,330 crore (US$ 13.07 billion) in FY23 compared to Rs. 95,000 crore (US$ 11.47 billion) in FY22 and Rs. 54,951 crore (US$ 6.63 billion) five years ago.
- India’s defence import value stood at US$ 463 million for FY20 and US$ 469.5 million in FY21. India targets to export military hardware worth Rs. 35,000 crore (US$ 5 billion) in the next five years.
- As of 2019, India ranked 19th in the list of top defence exporters in the world by exporting defence products to 42 countries. Defence exports in the country stood at Rs. 15,920 crore (US$ 1.94 billion) in 2022-23.
- Defence exports grew by 334% in the last five years and India now exports to over 75 countries due to collaborative efforts.
RECENT DEVELOPMENT/INVESTMENTS
- As of July 31, 2023, 393 startups/MSMEs/individual innovators have been engaged and 270 contracts have been signed.
- Indian and American startups will now be able to co-develop and co-produce advanced technologies, including in areas of space artificial intelligence, under the India-United States Defence Acceleration Ecosystem (INDUS-X).
- To promote indigenous design and manufacturing, funds have also been earmarked for procurement from indigenous sources.
- For FY24, funds have been earmarked in the ratio 67.75:32.25 between Domestic and Foreign procurement in the Capital Acquisition Budget of the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- In addition, the MoD has also directed spending an amount of Rs. 1,500 crore (US$ 181.1 million) towards procurement from start-ups.
- The 10th meeting of the Sub Committee on Military Cooperation between India and Malaysia was held in New Delhi on July 27, 2023.
- During the meeting, the existing defence cooperation between the two countries both sides explored effective and practical initiatives to further expand the bilateral defence engagements.
- The 8th India-Australia Defence Policy Talks (DPT) was held at Canberra in Australia on July 24-25, 2023. During the Defence Policy talks, both sides reviewed the bilateral defence cooperation between the two countries and explored new initiatives to further strengthen and deepen bilateral defence engagements.
- The Defence Minister, Mr. Rajnath Singh handed over two 'Made in India' platforms, a Fast Patrol Vessel and a Landing Craft Assault ship, to the Maldives National Defence Forces, during a visit to the country in May 2023.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
- The Central government aims to take India’s defence exports up to US$ 5 billion by 2024-25.
- Of the Union Budget for Financial Year 2023-24, the Ministry of Defence has been allocated a total Budget of US$ 72.2 billion (Rs. 5,93,537.64 crore), which is 13.18 % of the total budget. This includes an amount of US$ 16.8 billion (Rs. 1,38,205 crore) for Defence Pensions.
- The total Defence Budget represents an enhancement of US$ 8.3 billion (Rs. 68,371.49 crore) (13%) over the Budget of 2022-23.
- In the Union Budget 2023-24, the Capital Investment Outlay has been increased steeply for the third year in a row by 33 per cent to US$ 121 billion (Rs. 10 lakh crore), which would be 3.3 per cent of GDP. This will be almost three times the outlay in 2019-20.
- Accordingly, the Capital Allocations for modernization and infrastructure development of the Defence Services have been increased to US$ 19.7 billion (Rs. 1,62,600 crore) representing a rise of US$ 1.2 billion (Rs. 10,230 crore) (6.7%) over 2022-23.
- Also, the increase in the Capital Budget since 2019-20 has been US$ 7.2 billion (Rs. 59,200 crore) (57%).
- This increase is a reflection of the Government’s commitment towards sustainable augmentation in the area of modernization & infrastructure development of the Defence Services.
- The Capital Budget of Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has been increased by 43% to US$ 607.8 million (Rs. 5,000 crore) in 2023-24 as against US$ 425.8 million (Rs. 3,500 crore) in FY23. Also, the allocation under this segment has doubled in two years since FY22.
- This will boost the Border infrastructure thereby creating strategically important assets like Sela Tunnel, Nechipu Tunnel & Sela-Chhabrela Tunnel and will also enhance border connectivity.
- Additionally, the Union Budget 2023-24 has also announced the revamped Credit Guarantee scheme for MSMEs which will take effect from 1st April 2023 through infusion of US$ 1.09 billion (Rs. 9,000 Crore) in the corpus. This will enable additional collateral-free guaranteed credit of US$ 24.3 billion (Rs. 2 lakh crore).
- Further, the cost of the credit has also been reduced by about 1 per cent. This scheme will give a further fillip to the MSMEs associated with the Defence Sector.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 has provided Exempt-Exempt-Exempt (EEE) status to the Agniveer Fund.
- With Government initiatives, the expenditure on defence procurement from foreign sources which used to be 46% of the overall expenditure has reduced to 36% in the last four years i.e., 2018-19 to 2021-22.
- Under the Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative, four positive indigenization lists of 411 products have been promulgated by the Department of Military Affairs and Ministry of Defence to be manufactured domestically for the defence sector, instead of being sourced via imports.
Challenges faced by the Indian defence sector:
Geopolitical Tensions:
- India shares borders with neighbouring countries, leading to ongoing geopolitical tensions. This presents a continuous challenge for the Indian defence sector in terms of border security and preparedness for potential conflicts.
Modernization and Technological Upgradation:
- Keeping up with rapid technological advancements is a constant struggle. The defence sector needs to invest in modernizing its equipment, infrastructure, and capabilities to stay ahead and effectively address evolving security threats.
Budget Constraints:
- Limited financial resources pose a significant challenge. Balancing the need for modernization with budgetary constraints requires strategic planning and prioritization to ensure the optimal allocation of funds.
Terrorism and Insurgency:
- India faces internal security challenges, including terrorism and insurgency. The defence forces must be equipped to handle asymmetric warfare, counter-terrorism operations, and maintain internal stability.
Cybersecurity Threats:
- With the increasing reliance on technology, the defence sector is vulnerable to cyber threats. Securing critical infrastructure and sensitive information from cyber attacks is a pressing concern that requires constant vigilance and investment.
Procurement Processes and Delays:
- Bureaucratic red tape and delays in procurement processes can hinder the timely acquisition of essential defence equipment. Streamlining these processes is crucial for ensuring that the forces are adequately equipped when needed.
Human Resource Management:
- Recruitment, training, and retention of skilled personnel are vital for the effectiveness of the defence sector. Ensuring a motivated and capable workforce is an ongoing challenge, particularly in the face of competition from the private sector.
Way forward:
- The Indian government is focussing on innovative solutions to empower the country’s defence and security via ‘Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX)’, which has provided a platform for start-ups to connect to the defence establishments and develop new technologies/products in the next five years (2021-2026).
- Working through partner incubators, iDEX has been able to attract the start-up community to participate in the Defence India Start-up Challenge (DISC) programme.
- To boost the defence sector and increase the infusion of FDI, the government in September 2020 revised the regulations and permitted FDI under the automatic route up to 74% and 100% through the government route in any area, where it is likely to provide access to contemporary technologies.
- The Defence Ministry has set a target of 70% self-reliance in weaponry by 2027, creating huge prospects for industry players. Green Channel Status Policy (GCS) has been introduced to promote and encourage private sector investments in defence production to promote the role of the private sector in defence production.
- Given the government's emphasis on easing restrictions on foreign investment to achieve India's goal of an "Atmanirbhar Bharat," the growth trajectory of the Indian defence sector remains strong.
Closing thoughts
- There are no easy shortcuts to filling up capability gaps in the design and manufacturing of aircraft and their systems. In an oligarchic market, with a handful of design houses, and IPR hiccups, governmental policy and mentoring would be critical for fostering joint technology partnerships, joint ventures in manufacturing and public-public and public-private partnerships.
- All stakeholders, including the private sector, must upscale their R&D allocation substantially as technology transfer of key systems will be hard to come by. The Indian industry must rise in a globally networked environment.
- The best way forward is to have a clear vision to upscale our technological skills to achieve self-reliance or Aatmanirbharta.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India-is-fast-emerging-as-a-big-global-player-in-defence-sector-and-capabilities-of-its-security-forces-are-constantly-rising%2C-says-PM-Modi&id=471202#:~:text=2%3A10PM-,India%20is%20fast%20emerging%20as%20a%20big%20global%20player%20in,constantly%20rising%2C%20says%20PM%20Modi&text=Prime%20Minister%20Narendra%20Modi%20has,security%20forces%20are%20constantly%20rising.
https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/indias-growing-economic-power-matches-its-defence-capabilities-rajnath-singh-101698134327331.html

Shital Mahajan Makes History
Context
- Indian skydiver Shital Mahajan jumped off a helicopter from a height of 21,500 ft in front of the world's highest peak, Mt Everest.

Details
- She became the first woman to do so. Mahajan landed at Kalapatthar Peak at an altitude of 17,444ft.
- Mahajan is a well-known Indian skydiver who holds several skydiving records and is the recipient of the fourth highest civilian award, the Padma Shri in 2001.
Peaks of India:
|
Kangchenjunga
|
- As the third-highest mountain in the world, Kangchenjunga stands tall on the India-Nepal border. Its main peak is 8,586 meters (28,169 feet) high and is part of the Himalayan range.
|
|
Nanda Devi
|
- Situated in the Garhwal Himalayas, Nanda Devi is the second-highest mountain in India, with a height of 7,816 meters (25,643 feet). The Nanda Devi National Park, where it is located, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
|
|
K2 (Mount Godwin-Austen)
|
- Although the more significant part of K2 is in Pakistan, a portion of this second-highest mountain in the world lies in the Indian-administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
|
|
Saltoro Kangri
|
- Part of the Saltoro Range in the Himalayas, Saltoro Kangri is the highest point in the Saltoro Mountains and is also situated in the region of Jammu and Kashmir.
|
|
Sia Kangri
|
- Located in the Eastern Karakoram Range in Jammu and Kashmir, Sia Kangri is one of the highest peaks in India, standing at an elevation of 7,422 meters (24,350 feet).
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Shital-Mahajan-Makes-History%3a-First-Woman-to-Skydive-from-21%2c500-ft-Near-Mt-Everest&id=471323
.jpg)
India's wholesale inflation continues to decline
Context
- India's wholesale inflation persisted in negative territory for the seventh consecutive month, in October.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended
Details:
- According to data released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the wholesale price index (WPI) recorded a 0.52 per cent decline in October compared to the same period last year. Wholesale inflation recorded a contraction of 0.26 per cent in September.
- The Ministry of Commerce and Industry said in a statement that the negative rate of inflation in October 2023 is primarily due to a fall in prices of chemicals and chemical products, electricity, textiles, basic metals, food products, paper and paper products, etc. as compared to the corresponding month of the previous year.
- Data showed on Monday that retail inflation, based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), eased to 4.87 per cent in October compared to 5.02 per cent in September this year.
- The retail inflation is within the Reserve Bank of India's upper tolerance limit of 6 per cent.
- The Government has mandated the apex bank to maintain retail inflation at four per cent with a margin of two per cent on either side
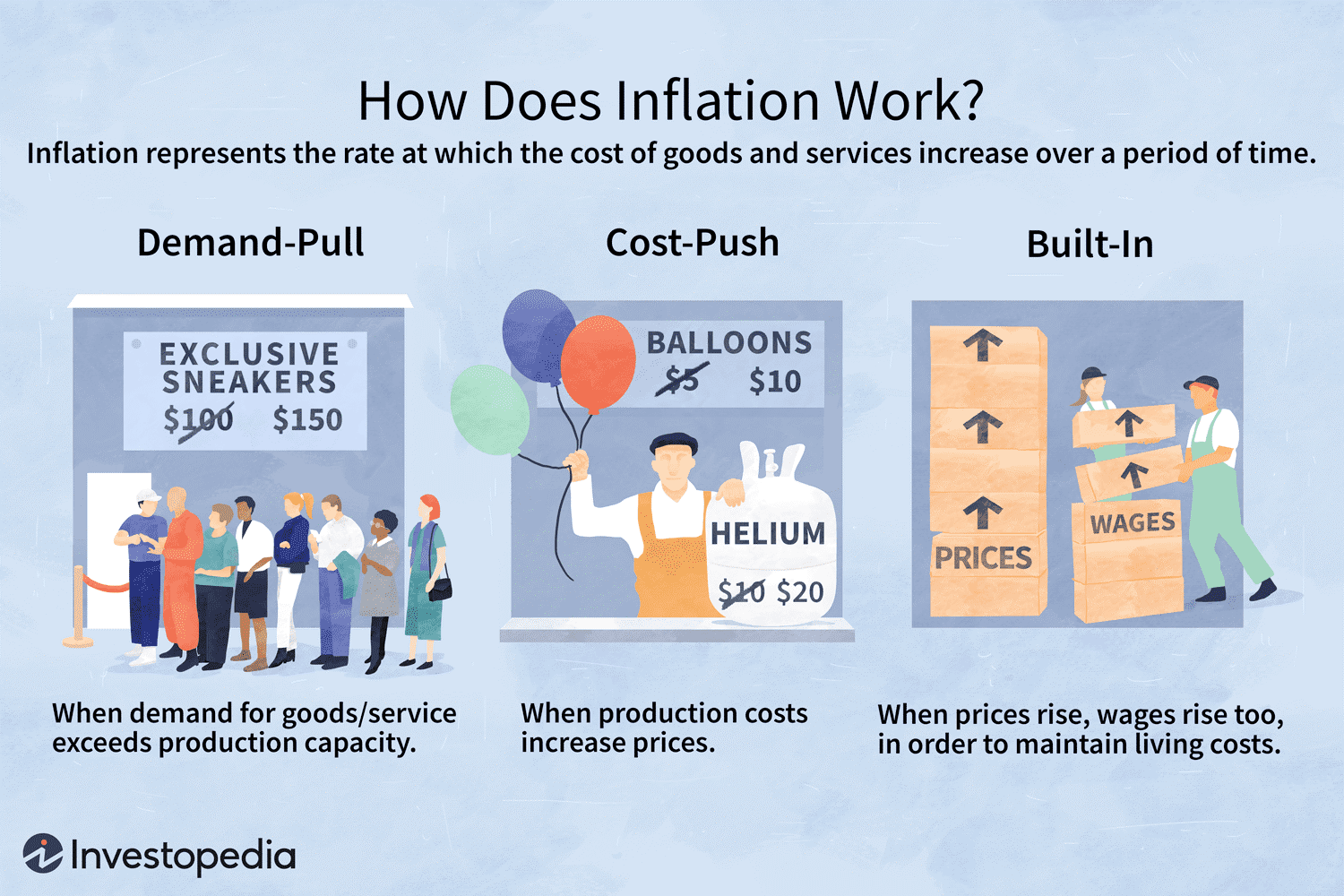
About Inflation:
| Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over some time. It results in a decrease in the purchasing power of a currency, as more money is required to buy the same quantity of goods and services. |
Types of Inflation:
Demand-Pull Inflation:
- Caused by an increase in aggregate demand for goods and services, surpassing the economy's ability to produce them.
- Often associated with periods of economic growth and increased consumer spending.
Cost-Push Inflation:
- Arises from an increase in the cost of production, such as rising wages or increased prices for raw materials.
- Can lead to a decrease in overall economic output.
Built-In Inflation (Wage-Price Inflation):
- Occurs when workers demand higher wages, and businesses pass on the increased labour costs to consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Creates a cycle where higher wages lead to higher prices, and vice versa.
Hyperinflation:
- Characterized by extremely high and typically accelerating inflation.
- Often associated with a collapse in the value of a country's currency, leading to a loss of confidence in the monetary system.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=India%26%2339%3bs-wholesale-inflation-continues-to-decline-for-seventh-consecutive-month%2c-in-October&id=471314

Global Media Congress
Context
- Abu Dhabi, 14th November 2023: The second edition of the Global Media Congress commences today at the Abu Dhabi National Exhibition Centre, UAE.

Details:
- Organised by the Emirates News Agency (WAM), under the patronage of Sheikh Mansour bin Zayed Al Nahyan, Vice President and Deputy Prime Minister of UAE, the three-day event brings together 257 brands, marking a 33 per cent increase from last year.
- The opening ceremony was AI-infused, with virtual anchors and avatars guiding the proceedings, adding a futuristic touch to the inauguration.
About Global Media Congress Overview:
|
Organizers
|
- The Global Media Congress (GMC) was organized by the ADNEC Group in collaboration with the Emirates News Agency (WAM).
|
|
Theme
|
- The theme of the GMC was "Shaping the Future of the Media Industry."
|
|
Format
|
- The GMC was a conference-cum-exhibition Congress aimed at providing a platform for international-level discussions on the challenges and opportunities in the media sector.
|
|
Participants
|
- The event attracted journalists, tech firms, content creators, digital marketing professionals, streaming giants, entertainment executives, regulators, and other important media stakeholders.
|
|
Exhibition
|
- The event featured an exhibition with more than 170 renowned media establishments and companies from 29 countries, showcasing the latest international technologies in media-related sectors.
|
|
Topics Discussed
|
- Discussions at the GMC covered a range of topics, including digital communications, the impact of artificial intelligence on contemporary media, and the integration of advanced technology and innovation in the media sector.
|
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Global-Media-Congress-Kicks-Off-in-Abu-Dhabi-exploring-Innovation-and-Sustainability&id=471285
Hamas designated as a terrorist organization
Context
- Israel Defense Forces (IDF) confirmed that it was carrying out a precise and targeted operation against Hamas in a specified area in the Al Shifa Hospital in a social media post in the wee hours on Wednesday.
Details:
- Eyewitness inside the hospital said that about 6 Israeli tanks and more than 100 commando soldiers had entered the hospital campus.
- The IDF had publicly warned that Hamas' continued military use of the Shifa hospital as a command post had jeopardized its protected status under international law.
- On Tuesday, the IDF alleged that they conveyed to the relevant authorities in Gaza to cease all military activities in the hospital within 12 hours. Both Israel and the US claim that Hamas has a command base under it which Hamas denies.
| Al-Shifa is the largest hospital in the Gaza Strip. Aid workers say the situation inside Al-Shifa is alarming and the Hamas-run health ministry says there are thousands of people using the complex to shelter from Israeli bombing. |
A short history of Hamas:
- Hamas is the largest Palestinian militant Islamist group and one of the two major political parties in the region. It is also designated a terrorist group by Israel, the United States, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and other countries.
- Formation and Early Years (1987-1993): Hamas, an acronym for Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiya (Islamic Resistance Movement), was established in 1987 during the First Intifada, a Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation.
- Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, a Palestinian cleric, played a key role in its formation. Hamas aimed to resist Israeli rule and promote its interpretation of Islamic principles in Palestinian territories.
- Charitable and Social Services: In its early years, Hamas focused not only on armed resistance but also on providing social and charitable services to Palestinians. It built schools, hospitals, and welfare programs, gaining support from some segments of the Palestinian population.
- Transition to Armed Resistance (1993-2000): Following the Oslo Accords in 1993, which aimed at establishing a framework for peace between Israel and the Palestinians, Hamas opposed the agreement, viewing it as compromising Palestinian rights.
- Designation as a Terrorist Organization: Hamas has been designated as a terrorist organization by several countries and entities, including the United States, the European Union, and Israel. Critics point to its use of violence against civilians and its rejection of the existence of the state of Israel as key reasons for the designation.
- Political Participation (2006-2007): In 2006, Hamas participated in Palestinian legislative elections and won a majority of seats.
- This led to its formation of a government, but internal conflicts with Fatah, the rival Palestinian faction, escalated into violence, resulting in the Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip in 2007.
- Gaza Strip Governance: Since 2007, Hamas has governed the Gaza Strip independently of the Palestinian Authority in the West Bank.
- The group's rule has faced international criticism for its methods of governance, restrictions on political dissent, and ongoing conflict with Israel.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Hamas-designated-as-a-terrorist-organization-by-several-countries&id=471321









