AIR SPOTLIGHT: NATIONAL CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK 2022 - DEVELOPING COMPETENCIES OF 21ST CENTURY
Context: Recently, the Union Education ministry launched the National Curriculum Framework for foundational stage education of children in the three to eight years age group.

National Curriculum Framework (NCF):
Features:
- The framework focuses on the 'panchakosha' concept- the ancient Indian emphasis on the body-mind connection.
- The NCF says its five parts are physical development(sharirik vikas), development of life energy (pranik vikas), emotional and mental development (manasik vikas), intellectual development (bauddhik vikas) and spiritual development (chaitsik vikas).
- The NCF 2022 for foundational age groups, a 360-page document, favours developing an interactive curriculum for children at various levels using story-telling techniques and real-life experiences. It says board games and stories from the Panchatantra (a collection of Indian fables and folk tales) should be used to teach children in the age group of 6-8 years.
- For the first three years of the foundational stage, that is 3 to 6 years, there should not be any prescribed textbooks. Rather, simple worksheets are more than sufficient to meet the curricular goals, says the document.
- It also recommends that the mother tongue should be the primary medium of instruction for children till eight years of age, in both public and private schools. English could be one of the second language options, it says, without giving any time-frame for introducing the language.
Process:
- As per the National Education Policy, 2020, following four NCFs will be developed:
- National Curriculum Framework for Early Childhood Care and Education (NCFECCE)
- National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCFSE)
- National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education (NCFTE) and
- National Curriculum Framework for Adult Education (NCFAE)
- In this regard, a comprehensive strategy has been worked out jointly by the Ministry of Education (MoE) and NCERT.
- As per this strategy, at the State level- all states/UTs will first prepare their State Curriculum Frameworks (SCFs) passing through the process of district level consultations, mobile app survey and development of position papers by the State Focus Groups in 25 areas/themes identified as per the NEP, 2020 including ECCE, Teacher Education and Adult Education.
- These draft SCFs will provide inputs to the development of NCFs. States/UTs and Autonomous organisation working under MoE, all will attempt this process to provide inputs for the NCFs. Recommendations of NEP, 2020 will be kept in view during the whole process.
- At the National level, NCERT will conduct a survey on MyGov Portal and get feedback from diverse stakeholders on the issues related to curriculum implementation. NCERT will also conduct 2-3 district level consultation in each of the states/UTs for collecting feedback from the grassroot level.
- Analysing inputs received from the district level consultations, states and national level survey on MyGov portal, National Focus Groups will prepare 25 position papers in the identified areas.
- Drawing insights from these position papers and draft SCFs, four NCFs will be prepared.
Key Highlights of National Education Policy 2020:
Multidisciplinary Institution
- By 2040, all higher education institutions HEIs) shall aim to become multidisciplinary institutions, each of which will aim to have 3,000 or more students.
- Aims at setting up at least one large multidisciplinary institution in or near every district by the year 2030.
- A university will mean a multidisciplinary institution that offers undergraduate and graduate programmes, with high quality teaching, research, and community engagement.
- Under Graded Autonomy, Academic, Administrative & Financial Autonomy will be given to colleges,on the basis of the status of their accreditation.
Undergraduate degree courses
- The undergraduate degree courses will be of either 3 or 4- year duration, with multiple exit options.
- A certificate course after completing 1 year in a discipline or field, including vocational and professional areas, or a diploma after 2 years of study, or a Bachelor’s degree after a 3-year programme.
- An Academic Bank of Credit ABC) shall be establishedwhich would digitally store the academic credits earned.
- Aims at 50% gross enrolment ratio by 2035.
- There will be multiple entry and exit options for those who wishto leave the course in the middle.
- Their credits will be transferred through Academic Bank of Credits.
- The National Testing Agency NTA) will offer a high-quality common aptitude test, as well as specialized common subject exams in the sciences, humanities, languages, arts, and vocational subjects, at least twice every year for university entrance exams.
Interaction with Foreign Institutions
- Aims at promotion India as a global study destinationproviding premium education at affordable costs.
- An International Students Office at each institution hosting foreign studentswill be set up.
- The Ministry has been renamed as Education Ministry.
- Selected universities like those from among the top 100 universities in the world will be facilitated to operate in India.
- High performing Indian universities will be encouraged to set up campuses in other countries.
Vocational Education
- The education ministry, would constitute a National Committee for the Integration of Vocational Education NCIVE).
- Students will get 360 degree holistic report card, which will not only inform about the marks obtained by them in subjects, but also their skills and other important points.
- Every child to learn at least one vocation and exposedto several more.
- Sampling of important vocational crafts, such as carpentry, electric work, metal work, gardening, pottery making, etc., as decided by States and local communities during Grades 6-8.
- By 2025, at least 50% of learners through the school and higher education system shall have exposure to vocational education
- A 10-day bag less period sometime during Grades 6-8 to intern with local vocational experts such as carpenters, gardeners, potters, artists, etc.
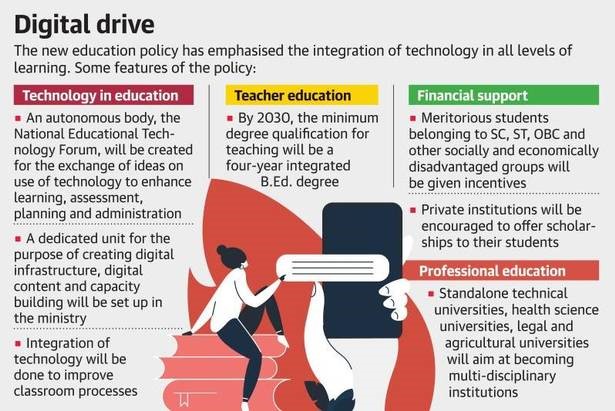
National Research Foundation
- A National Research Foundation NRF) will be established.
- The overarching goal of the NRF will be to enable a culture of research to permeate through universities.
- The NRF will be governed, independently of the government, by a rotating Board of Governors consisting of the very best researchers and innovators across
Vernacular Language
- Proposes the setting up of an Indian Institute of Translation and Interpretation IITI)while also laying significant emphasis on Sanskrit and other Indian languages.
- There will e- content in regional language apart from English and Hindi.
Online Education
- Quality technology-based options for adult learning such as apps, online courses/modules, satellite-based TV channels, online books, and ICT-equipped libraries and Adult Education Centres, etc. will be developed.
- A dedicated unit for the purpose of orchestrating the building of digital infrastructure, digital content and capacity buildingwill be created in the MHRD to look after the e-education needs of both school and higher education.
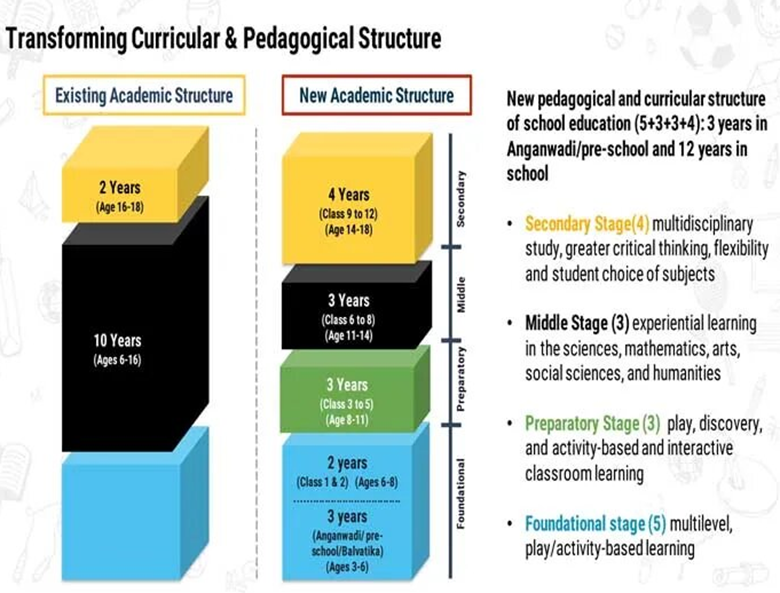
School Structure
- The extant 10+2 structure in school education will be modified with a new pedagogical and curricular restructuring of 5+3+3+4 covering ages 3-18.
- In the new 5+3+3+4 structure, a strong base of Early Childhood Care and Education ECCE) from age 3 is also included.
- Students of class 6 and onwards will be taught coding in schoolsas a part of 21st century skills.

Exam Structure
- In order to reduce the importance and stress of board exam, exam will be conducted in two parts: Objective and descriptive.
- Exam can be conducted twice a year. Board exam should promote knowledge application rather than rote learning.
Small Age Children
- A National Curricular and Pedagogical Framework for Early Childhood Care and Education NCPFECCE) for children up to the age of 8will be developed by NCERT.
- The planning and implementation of early childhood care and education curriculum ECCEC) will be carried out jointly by the Ministries of HRD, Women and Child Development WCD), Health and Family Welfare HFW), and Tribal Affairs.
- Prior to the age of 5 every child will move to a “Preparatory Class” or “Balavatika” that is, before Class 1), which has an ECCE-qualified teacher.
- Pre-school sections covering at least one year of early childhood care and education will be added to Kendriya Vidyalayas and other primary schools around the nation.
Gifted Children
- The nutrition and health including mental health) of children will be addressed, through healthy meals and regular health check-ups.
- NIOS will develop high-quality modules to teach Indian Sign Language, and to teach other basic subjects using Indian Sign Language.

Challenges in Indian Education System:
- India has achieved universal enrolment at the elementary level. This is a great achievement, but getting Students to School is only the beginning of human Capital formation.
- Poor quality of facilities, Shortage of qualified faculty.
- Out of date Curriculum, Limited university-industry Partnership.
- Indian origin Scientists have won the Nobel Prize, but post-independence work done in India has not led to a Science novel. If Indians Studying and working abroad can have a great impact, then obviously the problem has to do with our Systems of education and research.
- Broken governance System. There are few rewards for being a good teacher and few Punishments for being a Careless one. Need more effective and accountable governance Systems.
- The greed of Private Colleges to earn the maximum from every Student puts traumatic Pressure on Students which results in mental breakdown.
- More girls than boys drop out of School. While boys drop out to work, girls usually Stay at home and help with domestic Work. Social Conception of gender roles is an important factor.
- Learning loss due to pandemics and the digital divide.
Steps by the Government:
- The 86th Constitution Amendment provides the Fundamental right to free and compulsory education under Article 21Aincludes a Common education System where the “rich and Poor are educated under one roof".
- Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyanprovides funding to eligible State higher educational institutions.
- Declaration of Educational Institutions as institutions of Eminence,to provide world-class education to Indian Students within the Country.
- Creation ofHigher Education Financing Agency, for high-quality infrastructure in Premier educational institutions.
- National Institution Ranking Frameworkfor ranking our higher education institutions.
- GIANInitiative to invite distinguished academicians, entrepreneurs, scientists, and experts from premier institutions across the world to teach in higher educational institutions in India.
- SWAYAMPortal for online Courses.
- SWAYAM PrabhaProvide HD educational Channels through DTH on a 24X7 basis.
- Sodhganga to develop a national repository of universities in India, and digital Study material for higher education.
- Samagra Shiksha Schemeto ensure inclusive and equitable quality education at all levels of school education.
- The government is encouraging Open Online Courses via Swayam Platforms So that Students Can have access to quality lectures online.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to Provide Personalised instructions based on Student needs.
- The government needs to work on improving digital infrastructure and ensure that students have access to mobile phones or laptops.
Analysis of NCF:
- The National Curriculum Framework for foundational age children provides an “organic” and “well-framed” roadmap for teaching 3- to 8-year-olds, but would be difficult to implement in the absence of proper teacher training and infrastructural support, experts say.
- NCERT or, more specifically, the State Boards or SCERTs need to involve teachers as they are the primary stakeholders.
- NCERT and SCERTs need to identify the gaps in the current pedagogy so that the NCF could be implemented, failing which it would remain just a “another document”.
- Implementation would need “frugal” and “innovative” ideas that disrupt the resistance to change and resource constraints. The national guidelines should talk of how to implement rather than just stop at what to implement.
- It is most important to involve teachers in a big way. This kind of training for teachers has to be done with great urgency. Teachers have to be trained, whether it is on using the mother tongue or thematic concepts in pedagogy. We need to activate public and private agencies and involve Corporate Social Responsibility in teacher training.
- The government has to push financial support for schools in rural and tribal areas
https://www.livemint.com/education/news/education-minister-launches-national-curriculum-framework-for-foundational-stage-11666278215857.html

NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
HTT-40
Context: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi unveils indigenous trainer aircraft HTT-40, designed & developed by HAL, during DefExpo 2022.
Details:
- The aircraft has state-of-the-art contemporary systems and has been designed with pilot-friendly features.
- With over 60 per cent in-house parts and collaboration of private industry, it is a shining example of the vision of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
- The HTT-40 would be used for basic flight training, aerobatics, instrument flying and close formation flights whereas its secondary roles would include navigation and night flying.
- It is a testament to the cutting-edge technology designed to meet primary training requirements of the Indian defence services.
- Built around a meticulously-tested turbo-prop engine, the aircraft is equipped with the latest avionics, an air-conditioned cabin and ejection seats.
- It boasts of unique features like running change-over of pilots, hot-refuelling and short-turnaround time. All the tests required for certification were completed in record six years from the first flight.
- The HTT-40 has completed all systems tests, all PSQR performances, hot weather, sea level and cross wind trials and user assisted technical trials.
- It demonstrated rain water resistance.
- Provisional clearance for airworthiness of the aircraft is received from Centre for Military Airworthiness and Certification (CEMILAC).
https://newsonair.com/2022/10/19/pm-modi-unveils-state-of-art-indigenous-trainer-aircraft-htt-40-2/
NATIONAL CREDIT FRAMEWORK
In News
- The draft of the National Credit Framework (NCrF) was released by the Union Minister of Education and Minister of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Shri Dharmendra Pradhan.
- The Government has invited suggestions on the draft document.
Key points of the Draft National Credit Framework (NCrF)
- Taking forward the vision of the new National Education Policy (NEP), the Union Government has developed the National Credit Framework (NCrF).
- National Credit Framework is an umbrella framework for skilling, re-skilling, up-skilling, accreditation and evaluation in educational and skilling institutions and the workforce.
- The framework will promote Credits for knowledge acquisition, hands-on training, and positive social outcomes to achieve the target of 100% literacy in the next 2-3 years.
- NCrF will promote the integration of credits earned through school education, higher education and vocational and skill education by encompassing the National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF), National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) and National School Education Qualification Framework (NSEQF).
Objectives
- To allow students to move between educational institutions and enter and leave the program multiple times. The Framework is part of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
- Provide Flexibility in the duration of study courses through provisions of multiple entries and exit/work options.
- Allow Institutions to maintain digital records of credits earned by students.
- Promote the integration of academic and vocational disciplines to ensure flexibility and mobility between the two.
- Students can choose to study at one institution for a year and then transfer to another institution the following year.
- Allows students to complete courses online and earn credits. Educational institutions have the flexibility to adopt it when they choose.
- To support dropped-out students to re-enter the education ecosystem.
- To introduce reforms to incentivize knowledge, skills and experience.
Expected outcome
- National Credit Framework (NCrF) will establish multidisciplinary and holistic education with flexible curricula.
- It will open numerous options for students by integrating school and higher education with vocational education and experiential learning to promote skilling and vocational education.
- It will remove the hard distinction between the education streams and allow for more than one award in the same period by removing the distinction between arts, science, social sciences, commerce, etc.
- It will bring about a unification of higher education institutions to promote multidisciplinary education, creating a diverse and rich student knowledge base.
- It will promote strong collaboration between institutions and make credit mechanisms simpler and uniform.
- It will Increase focus on research and innovation, and Promote digital learning, and open distance learning.
- It will increase the enrolment of students, helping the government to fulfil the national vision of transforming India into the Skill Capital of the World.
- It will make students more employable by providing a more holistic designed multi/ cross-sectoral skills to youth.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Union-Minister-Dharmendra-Pradhan-launches-draft-of-National-Credit-Framework-for-public-consultation&id=449636
CYCLONE SITRANG
In News
- The developing cyclonic storm in the Bay of Bengal — Cyclone Sitrang — will bypass Odisha and make landfall near West Bengal-Bangladesh coasts on October 25, 2022, said the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
Details
- The India Meteorological Department forecasted that a low-pressure area is likely to form over the southeast and adjoining east-central Bay of Bengal.
- The low-pressure area in turn could intensify into a cyclonic storm that could affect Odisha, West Bengal, the northern part of Andhra Pradesh and adjoining areas.
The name Sitrang
- This cyclone, when it forms, could be named Cyclone Sitrang.
- The name Sitrang has been given by Thailand.
- Sitrang will follow cyclone Asani, which developed in the Bay of Bengal in early May this year. This will be the second cyclonic storm of 2022.
- The cyclones that are forming over the north Indian Ocean, including the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal, are given names by IMD. Thirteen members—Bangladesh, India, Iran, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen—are given warnings about tropical cyclones and storm surges by the IMD.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Cyclonic-Storm-Sitrang-makes-landfall-in-Bangladesh%2C-weakens-into-Depression&id=449840
IOR PLUS DEFENCE MINISTERS CONCLAVE
Context: Addressing the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) Plus Defence Ministers’ Conclave, Defence Minister Shri Rajnath Singh said that India is ready to supply missiles and weapon systems to friendly countries in the region.
Details:
About IOR+ Conclave:
- The first Indian Ocean Region (IOR) Defence Ministers’ Conclave was held in Bengaluru in February 2021.
- Building on the success of the first conclave, the Defence Minister hosted an IOR+ Defence Ministers’ Conclave in Gandhinagar, Gujarat recently for the year 2022.
- The broad theme was ‘Challenges Opportunities and Collaborations in the Indian Ocean’.
- The conclave was attended by 40 countrieslocated in the Indian Ocean region.
- It facilitated dialogue towards fostering a stable and peaceful Indian Ocean, with strategic and commercial partnerships within the IOR.
Significance of IOR+ Conclave:
- The conclave is an initiative to promote dialogue in an institutional and cooperative environment that can foster peace, stability & prosperity in the IOR.
- The forum has been named IOR+as the idea of this conclave is shared responsibility and prosperity.
- At the IOR+ conclave, Shri Rajnath Singh said that India was ready to supply weapons to friendly countries in IOR to help counter the challenges.
- Through IOR+ Conclave, India showcased three significant aspects of its commitment to foster peace and prosperity in the region –
- The first is readiness to convert its exhibition of its indigenously produced military hardware into a willingness to provide it to strategic partners in the Indian Ocean region.
- Secondly, there is a determined push by the government to enhance exports of defence production institutions in India.
- Thirdly, the defence production facilities of India now have a clear political backing for exports.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Defence-Minister-hosts-Indian-Ocean-Region-plus-Defence-Ministers%E2%80%99-Conclave-on-the-sidelines-of-DefExpo-2022&id=449614
RUSTOM-2
Context: The indigenous medium altitude long endurance (MALE) unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is expected to complete all user trials by August 2023
Details:
- It has been designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE), Bengaluru, with the production partners being Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd. (HAL) and Bharat Electronics Ltd.
- It is powered by a small turbofan engine. The engine is Russian TRDD-50MT originally designed for cruise missiles.
- It is being developed to carry out surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) roles and is capable of carrying different combinations of advanced payload and capable of auto landing, among others.
- Its navigation was done using GAGAN satellites through the onboard SATCOM system.
- High endurance UAVs are a priority requirement for the Indian armed forces especially in view of the stand-off with China in eastern Ladakh.
- Rustom-2 is also known as Tapas-BH(Tactical Airborne Platform for Aerial Surveillance-Beyond Horizon 201).
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/indigenous-uav-rustom-2-to-complete-user-trials-by-august-2023/article66032155.ece
MISSION LIFE
Context: The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi attended a bilateral meeting with UN Secretary-General, H.E. Mr Antonio Guterres and subsequently launched Mission LiFE at the Statue of Unity, Ekta Nagar, Kevadia, Gujarat.
Details:
PM on Mission LIFE:
- The Prime Minister remarked, The mantra of Mission Life is 'Lifestyle For Environment'.
- Emphasising the benefits of Mission LiFE, the Prime Minister said that it connects the powers of the people for the protection of this earth, and teaches them to utilise it in a better way.
- He underlined that Mission LiFE makes the fight against climate change democratic, in which everyone can contribute within their capacity.
- Mission LiFE believes that the environment can be protected by making changes in our lifestyle
- Mission LiFE makes us all trustees of the environment. A trustee is someone who does not allow indiscriminate use of resources. A trustee works as a nurturer and not as an exploiter
- The Prime Minister elaborated that Mission LiFE emboldens the spirit of the P3 model i.e. Pro Planet People. Mission Life, unites the people of the earth as pro planet people, uniting them all in their thoughts.
- It functions on the basic principles of ‘Lifestyle of the planet, for the planet and by the planet’.
- The Prime Minister quoted the Atharvaveda and recited, “‘Mata Bhumiah Putroham Prithivyah’ that is, the earth is our mother and we are her children.”
- The Prime Minister threw light on the concept of 'Reduce, Reuse and Recycle' and circular economy and mentioned that it has been a part of the lifestyle of Indians for thousands of years.
India’s commitment to addressing climate change:
- The total forest cover is 21.71% of the total geographical area in 2021, compared with 21.67% in 2019
- India’s forest cover is increasing and so is the population of lions, tigers, leopards, elephants and rhinos.
- The annual per capita carbon footprint in India is only about 1.5 tonnes, compared to the world average of 4 tonnes per year.
- Initiatives like Ujjwala Yojana, 75 ‘Amrit Sarovars’ in every district and unprecedented emphasis on waste to wealth.
- Today India has the fourth largest capacity for renewable energy in the world. India's renewable energy capacity has increased by about 290 percent in the last 7-8 years
- India has also achieved the target of achieving 40 percent of the electric capacity from non-fossil-fuel sources 9 years ahead of the deadline.
- India had also achieved a target of 10 percent ethanol blending in petrol, and that too 5 months before the deadline.
- Through the National Hydrogen Mission, India has moved towards an environment-friendly energy source. This will help India and many countries of the world to achieve their goal of net zero
- Highlighting the global campaign of One Sun, One World, One Grid, the Prime Minister remarked that India now wants to increase its partnership with the world even more while strengthening its resolve towards such goals.
- By leading the creation of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure, India has conveyed its concept towards environmental protection to the world. Mission LiFE is the next step in this series
Background:
- Mission LiFE aims at following a three-pronged strategy for changing our collective approach towards sustainability.
- First is by nudging individuals to practise simple yet effective environment-friendly actions in their daily lives (demand); second is by enabling industries and markets to respond swiftly to the changing demand (supply) and; third is to influence government and industrial policy to support both sustainable consumption and production (policy).
- The idea of LiFE was introduced by India during the 26th United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP26) in Glasgow in 2021.
- The idea promotes an environmentally conscious lifestyle that focuses on ‘mindful and deliberate utilisation’ instead of ‘mindless and wasteful consumption.
- With the launch of the Mission, the prevalent "use-and-dispose" economy governed by mindless and destructive consumption will be replaced by a circular economy, defined by conscious and deliberate consumption.
What are the Other Related Initiatives?
- National Afforestation Programme (NAP)
- National Mission for a Green India (GIM)
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- National Biodiversity Action Plan
- Rural Livelihood Schemes: Recognition of natural resources intrinsically linked to rural livelihoods is also reflected in flagship schemes like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) and the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM).
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=PM-Modi-launches-Mission-LiFE-movement-at-Kevadiya-in-Gujarat%3B-calls-for-lifestyle-change-to-protect-the-environment&id=449625








