AIR SPOTLIGHT: 13TH BRICS SUMMIT
CONTEXT: Prime Minister Modi chaired the 13th BRICS Summit virtually. It was the third time that India will be hosting the BRICS Summit after 2012 and 2016.
KEY POINTS:
- The theme of the Summit, chosen by India, was, BRICS@15: Intra-BRICS Cooperation for Continuity, Consolidation and Consensus.
- As Chair, India worked on specific deliverables across all three pillars of intra-BRICS cooperation in 2021.
- Political and Security: To enhance cooperation and dialogue on issues of global and regional security, developments in the global political space for peace, security and prosperity. Priorities under this pillar are:
- Reform of the Multilateral System
- Counter Terrorism Cooperation
- Economic and Financial: To promote economic growth and development for mutual prosperity through the expansion of intra-BRICS cooperation. Recognizing the advantages of using technological and digital solutions for the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals in BRICS countries with a special focus on:
- Implementation of the BRICS Economic Partnership Strategy 2020-25.
- Operationalization of the BRICS Agriculture Research Platform.
- Cooperation on Disaster Resilience.
- Innovation Cooperation.
- Digital Health and Traditional Medicine.
- Cultural and People to People: To qualitatively enrich and enhance intra-BRICS people to people contacts in cultural, academic, youth, sports, business, through regular exchanges.
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SUMMIT:
- PM’s Address:
- Highlighted the achievement of several new initiatives: Agreement on cooperation in the field of remote-sensing satellites; a virtual BRICS vaccine Research & Development Centre; BRICS Alliance on Green Tourism, etc.
- Highlighting the leading role that BRICS countries can play in the post-Covid global recovery, Prime Minister called for enhanced BRICS cooperation under the motto of 'Build-back Resiliently, Innovatively, Credibly and Sustainably'.
- Adopted BRICS Counter Terrorism Action Plan: It defines the approach and actions of the BRICS countries towards areas of Counter Terrorism cooperation which includes: Countering Radicalization and Online Terrorist Threats, Border Management, Information/ Intelligence Sharing, etc.
- Adopted Delhi Declaration: The declaration called for reforms of the principal organs of the United Nations including that of the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- International affairs:
- It also called for an “inclusive intra-Afghan dialogue” for stability in Afghanistan.
- Apart from Afghanistan, the BRICS leaders also took up the conflicts in Myanmar, Syria, the tension in the Korean peninsula, Israel-Palestine violence and other territorial disputes.
- Covid-19: Noted the proposal made by India and South Africa at WTO for the waiver of the TRIPS mechanism to ensure a rapid expansion of the Covid-19 vaccine production around the world.
HISTORY OF BRICS:
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- In 2001, the British Economist Jim O’Neill coined the term BRIC to describe the four emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
- It was the Russian side that initiated the creation of BRICS.
- On 20 September 2006, the first BRICS Ministerial Meeting was held at the proposal of Russian President Vladimir Putin on the margins of a UN General Assembly Session in New York. Foreign ministers of Russia, Brazil and China and the Indian Defence Minister took part in the meeting.
- They expressed their interest in expanding multilateral cooperation.
- On 16 May 2008, Yekaterinburg hosted Meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers on the initiative of Russia. After the meeting, a Joint Communique was issued, reflecting common stances on topical global development issues.
- On the Russian initiative on 16 June 2009, Yekaterinburg hosted the first BRIC Summit. BRIC Leaders issued a joint statement after the Summit.
- The document set forth the goals of BRIC “to promote dialogue and cooperation among our countries in an incremental, proactive, pragmatic, open and transparent way. The dialogue and cooperation of the BRIC countries is conducive not only to serving common interests of emerging market economies and developing countries, but also to building a harmonious world of lasting peace and common prosperity.”
- South Africa was invited to join BRIC in December 2010, after which the group adopted the acronym BRICS.
- The BRICS brings together five of the largest developing countries of the world, representing 41% of the global population, 24% of the global GDP and 16% of the global trade.
- The chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
- During the Sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (Brazil) in 2014, the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB - Shanghai, China). They also signed the BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement to provide short-term liquidity support to the members
SIGNIFICANCE OF BRICS FOR INDIA:
- The grouping provides India and China the opportunity to decouple their strategic contest from the other dimensions of the relationship.
- With the presence of Brazil and South Africa in the group, it provides is a low-cost way for India to signal its aspirations as a global power.
- BRICS’ repeated calls for reform of multilateral institutions, boosts India’s own assertions in this direction.
- India has remained the largest beneficiary of NDB loans so far.
- Thirty-four per cent of India's total imports are from the other four BRICS nations.
CHALLENGES FACED BY BRICS:
- The grouping bring together a mix of democratic and authoritarian regimes, with very different societal structures, resource bases, developmental trajectories, and historical traditions.
- The current pandemic has exacerbated pre-existing differences amongst the BRICS.
- From South Africa, along with other African countries, China has attracted criticism for the ill-treatment that has been meted out to African residents there.
- Suspicions among members about Chinese regional and global ambition may impact group’s functioning in future.
- BRICS does not have the ‘strategic vision’ to deal with ‘global matters’ on its own. For this, it relies on other international organisations.
- If the US-China rivalry intensifies, the already complex dynamics between India and China, India’s balancing act with the US, the growing Russia-China linkages, Russia-US tensions — raise the prospects of an ‘internal split.’
- BRICS do not have the funds to outcompete the Bretton Wood Institutions, the World Bank and IMF.
- Intra-BRICS trade and investment flows are very low.
CONCLUSION:
- The future of BRICS will depend on how much the leaders have agreed to stand collectively against trade protectionism, increase investments and share a global political agenda.
- The BRICS nations need to move towards a bottom-up approach to increasing private sector and citizen involvement.
- COVID provides an opportunity for the group to accelerate the establishment of the BRICS vaccine research and development centre as agreed in 2018.
- Building a collective strategy and identifying priority processes to implement it can ensure that BRICS cooperation deepens and becomes self-reinforcing
https://brics2021.gov.in/13th-summit
https://www.mea.gov.in/press-releases.htm?dtl/34239/Prime+Minister+chairs+13th+BRICS+Summit
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/brics-seeks-inclusive-intra-afghan-dialogue/article36390830.ece
NEWS IN BRIEF: PRELIMS SPECIAL
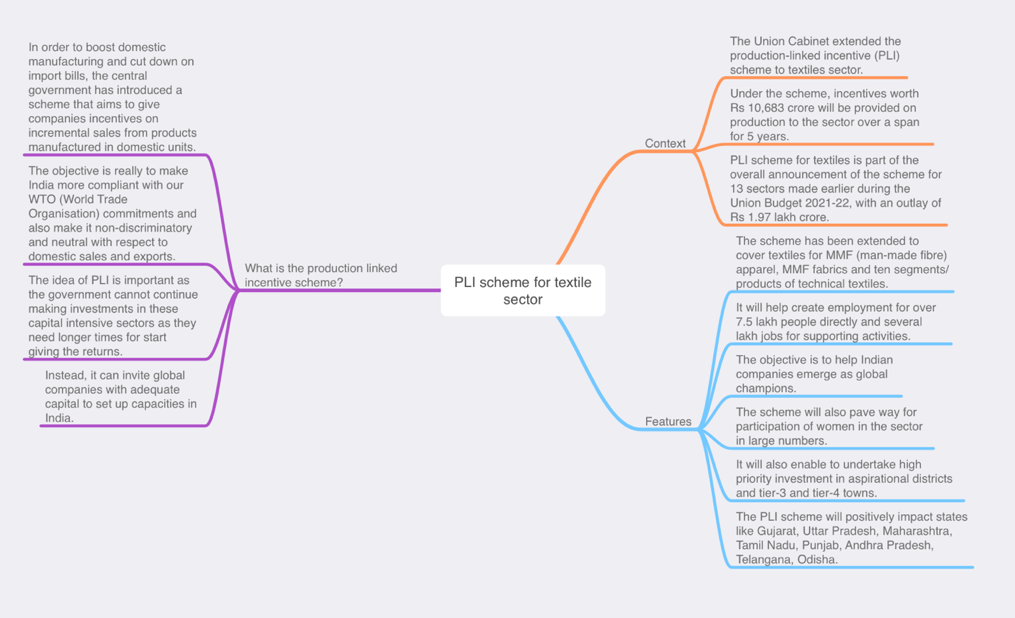
PLI SCHEME FOR TEXTILES
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/09/pli-scheme-for-textiles/
C-295MW FOR INDIAN AIR FORCE
- The Cabinet Committee on Security approved the procurement of 56 C-295MW transport aircraft from a Spanish company for the Indian Air Force.
- Sixteen aircraft will be delivered in flyaway condition from Spain within 48 months of signing of the contract and forty aircraft will be manufactured in India by TATA Consortium within ten years of signing of the contract.
- This is the first project of its kind in which a military aircraft will be manufactured in India by a private company.
- C-295MW aircraft is a transport aircraft of 5-10 Tonne capacity with contemporary technology.
- This will replace the ageing Avro aircraft of IAF.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/09/mega-2-5-3-billion-deal-for-indian-air-force-to-bring-onboard-56-most-versatile-efficient-tactical-transport-aircraft-c-295-mw/
NAGA PEACE PROCESS
- The Government of India has entered into a Ceasefire Agreement with National Socialist Council of Nagaland (K) Niki Group, with effect from 8th September, 2021 for a period of one year.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/09/centre-signs-ceasefire-agreement-with-national-socialist-council-of-nagaland-k-niki-group-for-one-year/
PRADHAN MANTRI GRAMIN DIGITAL SAKSHARATA ABHIYAN (PMGDISHA)
- PMGDISHA campaign for 100 percent digital literacy in Digital Villages
- Under the campaign, a three day certification drive for rural citizens, especially women and disadvantaged communities, will be conducted for a few days in September 2021.
- The drive has been launched under the PMGDISHA Scheme, the flagship digital literacy programme of GOI.
- Apart from this, Common Service Centres (CSC) also proposed to make all the Digital Villages 100 percent Digital Literate.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=Around-5-cr-beneficiaries-enrolled%2C-over-4-cr-trained-under-PM-Gramin-Digital-Saksharta-Abhiyan-Scheme-so-far&id=423630
MEDIUM RANGE SURFACE TO AIR MISSILE (MRSAM) SYSTEM
- DRDO handed over air defence missile (MRSAM) System to the Indian Air Force.
- The MRSAM (IAF) is an advanced network centric combat Air Defence System developed jointly by DRDO and Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) in collaboration with the Indian industry comprising of private and public sectors including MSMEs.
- It is capable of engaging multiple targets at ranges up to 70 kms in severe saturation scenarios.
- The missile is powered by an indigenously developed rocket motor and control system for achieving high manoeuvrability during the terminal phase.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/10/make-in-india-induction-of-mrsam-barak-8-missile-system-into-indian-defence-forces/
INDIA RANKINGS 2021
- Education Minister released the India Rankings 2021 instituted by the National Institutional Ranking Framework.
- This is the sixth consecutive edition of India Rankings of HEIs in India.
- Over the years, three new categories and five new subject domains were added to bring the total tally to 4 four categories and 7 subjects.
- Four categories are: Overall, University, College, Research Institutions
- Seven subjects are: Engineering, Management, Pharmacy, Architecture, Medical, Law, Dental
- Research institutions have been ranked for the first time in India Rankings 2021.
- Indian Institute of Technology Madras retains the first position in the Overall Category as well as in the Engineering Category for the third consecutive year.’
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru tops the University as well as Research Institution category (this category was introduced for the first time in 2021).
- IIM Ahmedabad tops in Management subject.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi occupies the top slot in Medical subject.
- Jamia Hamdard tops the list in Pharmacy subject.
- Miranda College retains the first position amongst colleges for the fifth consecutive year.
- IIT Roorkee takes the top slot for the first time in Architecture subject displacing IIT Kharagpur.
- National Law School of India University, Bangalore retains its first position in Law.
- Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal, secures the first position in “Dental” category.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/09/nirf-rankings-2021-iit-madras-tops-rankings-in-overall-category/
‘MAIN BHI DIGITAL 3.0’
- ‘Main Bhi Digital 3.0’ – A special Campaign for Digital Onboarding and Training for street vendors launched.
- The campaign has been launched by the Ministry of Housing Affairs in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology across 223 cities in the country.
- The drive is a part of the PM SVANidhi scheme.
- The BharatPe, Mswipe, PhonePe, Paytm, Aceware are participating in this drive to issue UPI IDs, QR code and provide digital training.
- Digital Payment Aggregators will handhold the street vendors to bring about enhanced adoption of digital transactions and behaviour change.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/10/govt-launches-main-bhi-digital-3-0-campaign-for-digital-onboarding-training-for-street-vendors/
SWACHH SURVEKSHAN GRAMEEN (SSG) 2021
- The Swachh Survekshan Grameen 2021 was launched under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen) Phase II.
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) will undertake the Survekshan (survey) countrywide to support the acceleration of ODF Plus interventions and increase momentum for improving ODF Sustainability as well as Solid and Liquid Waste Management (SLWM) activities across villages.
- More than 17000 villages in 698 districts will be covered this time.
- In the SSG 2021, many new elements including Assessment of Solid, Liquid, Plastic Waste & faecal Sludge Management Arrangements, Awareness on Menstrual Hygiene and Management & Disposal Arrangements for Menstrual Waste have been included.
https://newsonair.com/2021/09/09/swachh-survekshan-grameen-2021-to-be-launched-under-swachh-bharat-mission-phase-2-today/




