PERSPECTIVE: Combating Deepfakes
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Deepfake has emerged as a serious threat to democracy and social institutions across the world.
Details:
- Propagation of deepfake content via social media platforms has aggravated this challenge.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has, from time to time, advised social media platforms to exercise due diligence and take expeditious action against deepfake.
- IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw recently interacted with representatives from academia, industry bodies and social media companies on the need to ensure effective response to deepfake.
- It was further agreed that within the next 10 days, actionable items on four pillars would be identified including Detection, Prevention, Reporting and creating awareness.
- The Centre will soon appoint an officer to take appropriate action against such content.
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) also advised social media intermediaries to exercise due diligence and take expeditious action against deepfakes.
- Detection: Deepfake content should be detected before and after such content is posted.
- Prevention: There should be an effective mechanism for preventing propagation of deepfake content
- Reporting: Effective and expeditious reporting and grievance redressal mechanism should be available
- Awareness: Mass awareness on the issue of deep
|

About Deepfake:
| Deepfake technology poses a multifaceted threat, impacting individuals, democracies, and global security. This artificial intelligence-driven tool can manipulate media, presenting a range of challenges across various domains. |
Introduction to Deepfake Technology
- Deepfake technology, a portmanteau of "deep learning" and "fake," refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to create or manipulate audio and visual content to generate realistic but fabricated media.
- While initially popularized for entertainment purposes, deepfake technology has raised concerns due to its potential misuse, posing significant challenges to various aspects of society.
Understanding the Mechanism of Deepfake Creation
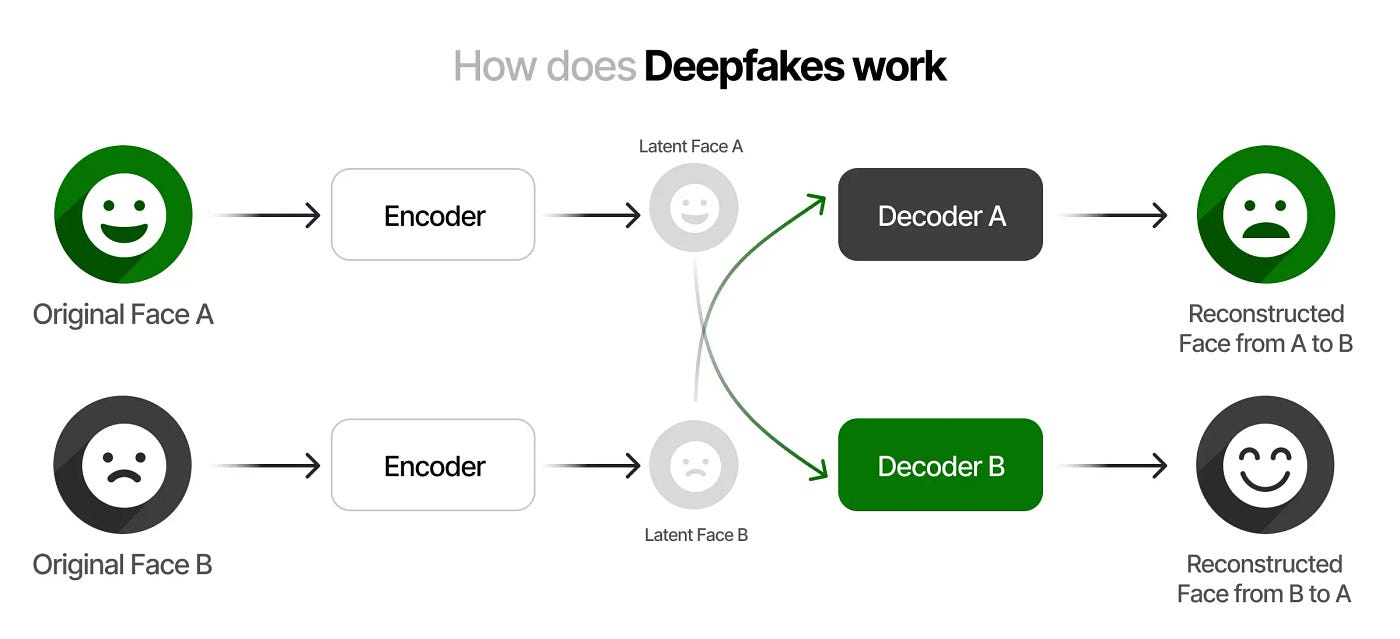
- Deep Learning Algorithms: Deepfake technology employs sophisticated deep learning algorithms, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and autoencoder models, to analyze and synthesize realistic human faces, voices, and gestures.
- Data Training and Mimicry: By analyzing large datasets of images and videos, deepfake algorithms learn to mimic facial expressions, speech patterns, and other human characteristics, enabling the creation of convincing and deceptive digital content.
Dangers Associated With Deep Fake:
National Security Implications
- New Front of Warfare: Deepfakes emerge as a potent weapon for nation-states, allowing them to sow discord and uncertainty. By fabricating convincing narratives, geopolitical adversaries can destabilize target countries, jeopardizing public safety and political stability.
- Nation-State Manipulation: Actors with geopolitical motives, ideological beliefs, or economic agendas can exploit deepfakes to shape media narratives, fostering chaos and mistrust. Insurgent groups and terrorists leverage this technology to manipulate sentiments against states, posing threats to national security.
Targeting Women: A Disturbing Dimension
- Malicious Exploitation: Deepfakes, particularly in the realm of pornography, become a tool for emotional and reputational harm. Primarily targeting women, these manipulations inflict psychological trauma, perpetuating harmful stereotypes and reducing individuals to mere sexual objects.
Damage to Personal and Professional Reputation
- Reputational Sabotage: Deepfakes can tarnish personal and professional reputations by depicting individuals engaging in antisocial behaviors or expressing vile sentiments. The aftermath can be severe, impacting lives and careers even after debunking the falsehood.
- Extortion and Exploitation: In a disturbing turn, deepfakes can be weaponized for financial gain or extracting confidential information. Perpetrators leverage the threat of reputational damage to extort money or coerce individuals into compromising positions.
Undermining Democratic Processes
- Manipulating Discourse: Deepfakes wield the potential to alter democratic discourse, eroding trust in institutions and impairing diplomacy. False narratives, fueled by deepfakes, can manipulate public perception about institutions, policies, and politicians, fostering a climate of misinformation.
- Election Disruption: A high-quality deepfake of a political candidate, strategically deployed before an election, can tarnish their image and influence outcomes. The technology can inject compelling false information, casting doubt on the legitimacy of elections and sowing seeds of division.
Fueling Polarization and Suppressing Dissent
- Effective Tool for Polarization: Deepfakes amplify societal divisions, becoming a tool for leaders to consolidate power and spread populist narratives. By suppressing dissent and manipulating information, these fabrications contribute to the polarization of societies.
- Silencing Dissent: Leaders can exploit deepfakes to silence dissent by discrediting opposition figures or spreading misinformation. The technology's effectiveness lies in its ability to create convincing narratives that resonate with targeted audiences.

Applications and Implications of Deepfake Technology
- Entertainment Industry: Deepfake technology has found applications in the entertainment industry, enabling the creation of engaging visual effects, digital doubles, and realistic character animations in movies and video games.
- Social Media and Misinformation: The proliferation of deepfake content on social media platforms has amplified concerns about the spread of misinformation, as manipulated videos and audio recordings can deceive the public and influence public opinion.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Deepfakes pose significant cybersecurity threats, as malicious actors can utilize this technology for identity theft, impersonation, and fraud, jeopardizing the security and privacy of individuals and organizations.
- Political Manipulation and Disinformation: The potential use of deepfake technology for political manipulation and disinformation campaigns raises concerns about the integrity of democratic processes and public trust in political institutions.
Ethical and Legal Implications of Deepfake Technology
- Privacy and Consent: Deepfake technology raises critical questions about privacy and consent, especially concerning the use of individuals' images and voices without their explicit permission.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: The potential for identity theft and fraud through the creation of convincing fake identities using deepfake technology necessitates robust legal frameworks to deter and penalize such malicious activities.
- Impacts on Journalism and Media Integrity: Deepfakes have the potential to undermine the credibility of journalistic content and media integrity, challenging the authenticity and trustworthiness of audiovisual evidence.
- Regulatory Challenges: Addressing the ethical and legal implications of deepfake technology requires the formulation of comprehensive regulatory frameworks that balance innovation and freedom of expression with the protection of individuals' rights and societal integrity.
Measures to be taken:
Enhancing Media Literacy
| Media literacy serves as a powerful tool against disinformation and deep fakes. Strengthening efforts in media literacy is essential to equip both consumers and journalists with the skills to discern and navigate the complex landscape of information. |
- Consumer Empowerment: Improving media literacy empowers consumers to decipher, understand, and critically evaluate information. A well-informed public is better equipped to identify deep fakes and mitigate their impact.
- Journalistic Competence: Media literacy efforts should focus on enhancing the capabilities of journalists to navigate digital media and verify sources. Journalists play a crucial role in shaping a credible information ecosystem.
- Short Interventions: Even brief interventions in media literacy, where individuals learn to recognize motivations and contextualize information, can significantly reduce the harm caused by deep fakes.
Need for Regulation
| Implementing meaningful regulations, developed through collaborative discussions with the technology industry, civil society, and policymakers, is imperative to create a deterrent against the creation and dissemination of malicious deep fakes. |
- Collaborative Regulation: Regulations should be crafted through inclusive discussions involving various stakeholders. A collaborative approach ensures that regulations are effective and ethical, and consider diverse perspectives.
- Technology Industry Involvement: Engaging the technology industry in regulatory processes is essential. Cooperation with tech companies can lead to the development of effective measures to prevent the misuse of technology for creating deep fakes.
Technological Interventions
| The development and implementation of accessible technology solutions are crucial for detecting deep fakes, authenticating media content, and amplifying authoritative sources. |
- Detection Technology: Easy-to-use technology solutions for detecting deep fakes play a pivotal role. These tools should be accessible to a wide range of users, from individuals to institutions, fostering a collective defense against misinformation.
- Authentication Tools: Technology that enables the authentication of media content can bolster the credibility of information. Implementing reliable authentication measures contributes to building trust in digital content.
Behavioral Change
| Addressing the menace of deep fakes requires a societal shift in behavior, emphasizing critical consumption of media, thoughtful sharing on social platforms, and active participation in countering the infodemic. |
- Critical Media Consumption: Society must adopt a critical mindset when consuming media on the internet. Questioning and verifying information before accepting and sharing it can significantly reduce the spread of deep fakes.
- Responsible Social Media Sharing: Individuals should pause and reflect before sharing content on social media platforms. Responsible sharing practices contribute to curbing the dissemination of misleading information.
- Community Engagement: Society as a whole needs to actively engage in countering the infodemic. Collaborative efforts, including community-based initiatives, can foster a sense of collective responsibility in tackling the challenges posed by deep fakes.
India's Current Stand on Deepfakes
- Existing Laws: India relies on pre-existing laws, such as Sections 67 and 67A of the Information Technology Act (2000), which may apply to some aspects of deepfakes, including defamation and explicit material dissemination.
- Defamation Provision: Section 500 of the Indian Penal Code (1860) offers punishment for defamation, which can be applied in cases involving deepfakes.
- Personal Data Protection Bill (2022): Although this bill might provide some protection against the misuse of personal data, it doesn't explicitly address the issue of deepfakes.
- Lack of Comprehensive Legal Framework: India lacks a comprehensive legal framework dedicated to regulating deepfakes, despite their potential implications for privacy, social stability, national security, and democracy.

Conclusion
Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration for Truth and Freedom
| Defending truth and safeguarding freedom of expression demands a comprehensive strategy involving various stakeholders and diverse approaches. A multi-modal approach, combining legislative regulations, platform policies, technology intervention, and media literacy, offers ethical countermeasures to effectively mitigate the threat of malicious deep fakes. |
- Legislative Regulations: Enacting robust legislative frameworks is a fundamental step. Collaborative efforts among lawmakers, legal experts, and civil society can formulate regulations that strike a balance between protecting freedom of expression and curbing the misuse of technology for malicious purposes.
- Platform Policies: Social media platforms, as key disseminators of information, play a crucial role. Collaboration between these platforms, policymakers, and user communities can lead to the development and enforcement of policies that deter the creation and dissemination of harmful deep fakes.
- Technology Intervention: Active involvement in the technology industry is essential. Collaborating with tech companies ensures the development of cutting-edge tools for detecting and preventing deep fakes. This partnership promotes responsible innovation and ethical use of technology.
- Media Literacy Initiatives: Empowering individuals through media literacy is a cornerstone of the strategy. Collaborative actions between educational institutions, media organizations, and technology experts can enhance public awareness and critical thinking skills, enabling a discerning public that navigate the digital information landscape effectively.
Ethical Countermeasures for Deep Fake Threats
By integrating the strengths of legislative, technological, and educational approaches, multi-stakeholder collaboration fosters a holistic defense against the challenges posed by deep fakes. This approach not only protects truth and freedom of expression but also promotes a resilient and well-informed society capable of withstanding the impact of misinformation and disinformation.
CITATIONS:
https://sansadtv.nic.in/episode/perspective-combating-deepfakes-24-november-2023
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1979042
https://www.thestatesman.com/india/deepfakes-row-govt-to-assist-people-in-filing-fir-against-social-media-cos-1503243778.html
https://www.fortuneindia.com/enterprise/govt-to-announce-rules-to-curb-deepfake-content-on-social-media/114837
https://pub.aimind.so/deep-fake-a-test-to-reality-86e9d1e19cba
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/05/how-can-we-combat-the-worrying-rise-in-deepfake-content/




